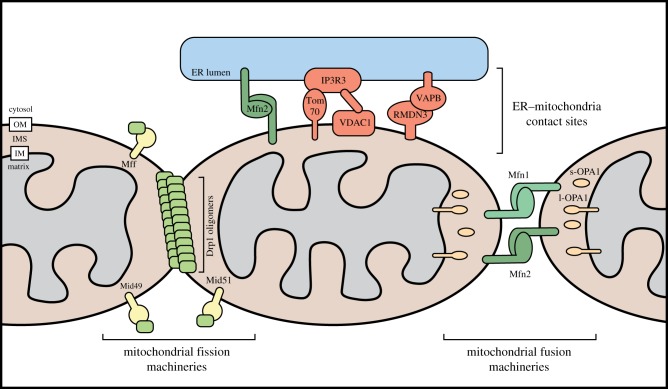
Figure 2.
Cellular machineries mediating mitochondrial fission, fusion and formation of contact sites with the endoplasmic reticulum. Mitochondria continuously undergo fission and fusion. Fission is mediated by the GTPase Drp1, which can be recruited to the outer mitochondrial membrane by a variety of receptors, including Mff, Fis1, Mid49 and Mid51. Drp1 at the outer membrane can oligomerize into fibrils that constrict mitochondria to initiate fission. Mitochondrial fusion is initiated by tethering of mitochondria through homotypic interactions between Mfn1 and Mfn2 on opposing mitochondria. Inner membrane fusion is mediated by OPA1, which exists as long and short forms generated through proteolysis. Contact sites between the mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) are established and maintained through protein–protein interactions. Interactions occur between Mfn2 molecules on the ER membrane and the outer mitochondrial membrane, and between VAPB on the ER membrane and RMDN3 on the mitochondrial outer membrane. Interactions also occur between IP3R3, a calcium channel on the ER membrane, and VDAC1 and hTom70 on the mitochondrial outer membrane.