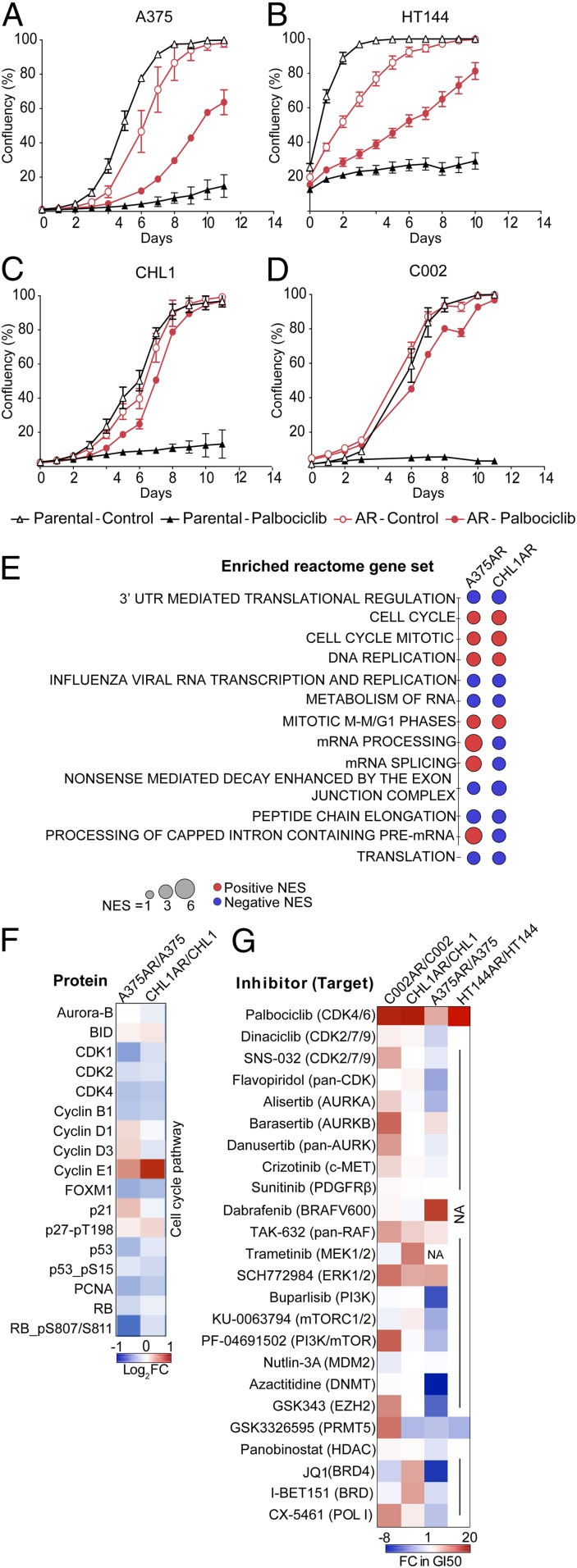
Fig. 1.
Resistance to palbociclib is associated with increased sensitivity to PRMT5 inhibition. (A–D) Proliferation curves of the parental and acquired-resistant cell lines treated with 2 μΜ palbociclib or vehicle. Graphs are representative of three independent experiments. Error bars represent SEM for 3 technical replicates. (E) Dot plot of commonly enriched Reactome gene sets using RNA-seq on A375AR and CHL1AR cells compared to their parental counterparts. Normalized enrichment score (NES) ≥ 2.00 or ≤ −2.00, false discovery rate (FDR) ≤ 0.01. (F) Heat map showing RPPA analysis of changes in cell cycle targets in A375AR and CHL1AR compared to their parental counterparts. (G) Heat map showing the changes in GI50 (sensitivity) to a panel of targeted therapies in resistant cell lines compared to the parental counterparts (red represents reduced sensitivity in palbociclib-resistant cells, and blue represents increased sensitivity in palbociclib-resistant cells).