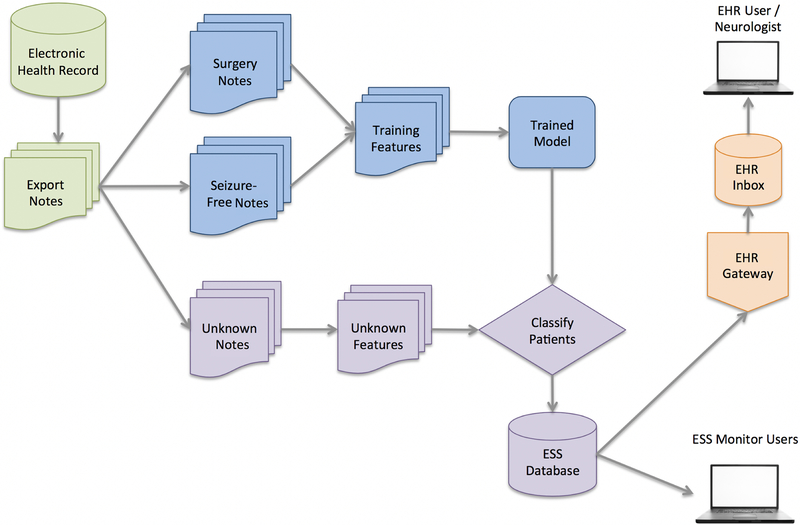
Figure 1.
Architecture of the natural language processing (NLP) algorithm. Electronic health record (EHR) data from all epilepsy patients were exported from the operational database (upper left). Patients with epilepsy were split into three groups: 1) patients who had a history of epilepsy surgery; 2) patients who were seizure free; and 3) “unknown” patients. The NLP algorithm was trained using patients from the first two groups (“Surgery” and “Seizure-Free”), and the trained model was used to assign patients in the “Unknown” group a surgical candidacy score. The scores were then stored in the epilepsy surgery software (ESS) database, where they could be accessed by the study team or used to send alerts to neurologists (shown on right).