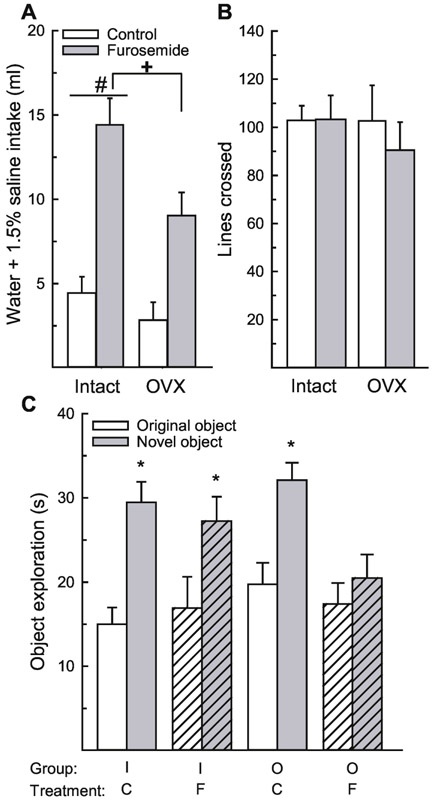
Figure 4.
Ovarian hormones protect against hypovolemic dehydration-induced memory impairments in the novel object recognition paradigm. (A) Rats treated with furosemide consumed significantly more water and 1.5% saline compared to rats treated with saline control, which confirmed that the treatment induced dehydration. In addition, intact rats consumed more than OVX rats. (B) There was no difference in activity between any group. (C) Both groups of intact rats and control-treated OVX rats spent significantly more time investigating the novel, compared to the original object. Furosemide-treated OVX rats spent a similar amount of time investigating the novel and original object. Abbreviations: intact (I), ovariectomized (O), saline control (C), furosemide (F). Hashed bars denote the treatment groups. +Greater than control-treated rats, p < 0.001. #Greater than OVX rats, p = 0.009. *Greater than time investigating original object, p < 0.001.