Figure 2.
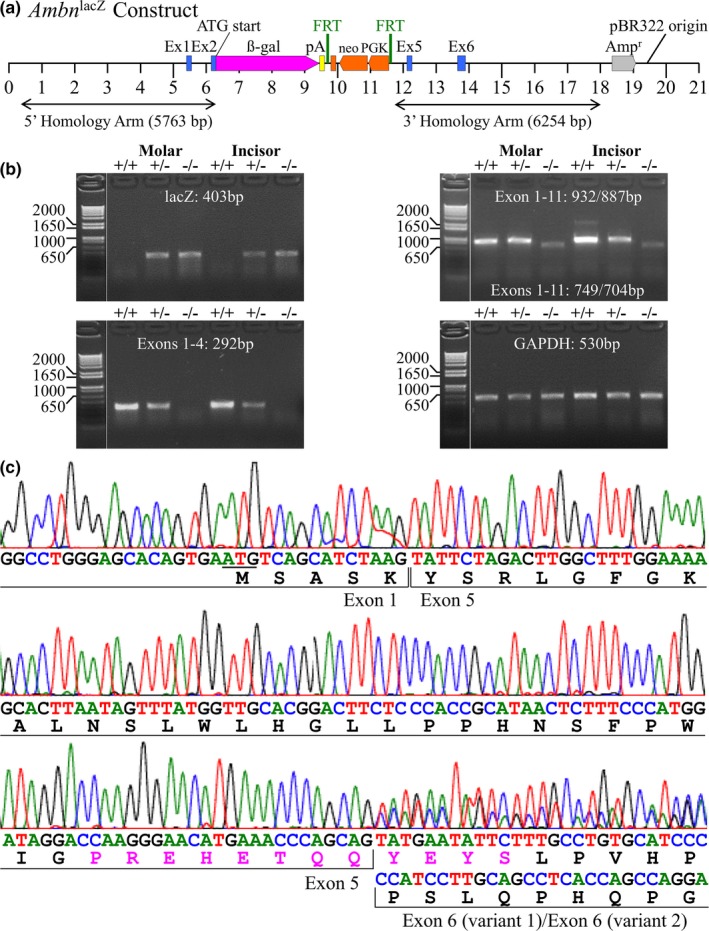
Ameloblastin knockout/NLS‐lacZ knockin mouse (Ambn lacZ/lacZ) generation and RT‐PCR verification. (a) Diagram of the Ambn lacZ construct used to delete 4,204 bp from the 5' end of the mouse C57BL/6J Ambn starting with the translation initiation codon in Exon 2 and ending in Intron 4. The deleted segment encoded 56 amino acids including the signal peptide, signal peptide cleavage site (after Ala26) and key phosphorylated residues, Ser20 and Ser22. This 4,204 bp segment was replaced with NLS‐lacZ encoding ß‐galactosidase with a nuclear localization signal (NLS) followed by two downstream polyadenylation signals (pA) and an FRT‐PGK‐neo‐FRT selection cassette [that expressed a neomycin (neo) resistance gene driven by the mouse phosphoglucokinase (PGK) gene promoter]. After the selection cassette was excised by Flp recombinase, the size of the insert was 3,419 bp. The sequences of Ambn+/+ and Ambn lacZ are provided in Figures S3, S4 respectively. (b) Ethidium bromide stained agarose gels showing RT‐PCR amplified mRNA extracted from D5 mouse first molar enamel organ epithelium. (c) Chromatography showing partial sequence of Ambn lacZ/lacZ mouse cDNA amplified by primers in Exon 1 and 11. Amino acids colored in magenta indicate epitope used to generate AMBN antibody
