Figure 3.
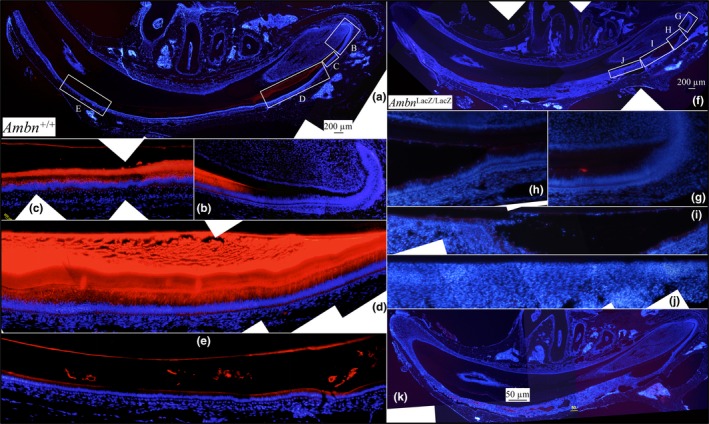
Immunohistochemistry of hemi‐mandible longitudinal sections of 7‐week Ambn +/+ (a‐e) and Ambn lacZ/lacZ (f‐k) incisors using an antibody raised against the AMBN peptide CMRPREHETQQYEYS. Red stain is AMBN; blue is nuclei stained with 4',6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole (DAPI). (a) Low magnification montage of WT section. Boxes labeled B‐E show positions of high magnification montages below. (b‐d) Strong AMBN signal is observed in secretory stage ameloblasts and the enamel extracellular matrix. (e) Much weaker AMBN signal is observed in maturation stage ameloblasts in the maturing enamel matrix. (f, k) Low magnification montages of Ambn lacZ/lacZ mouse sections. Boxes in f labeled g‐j indicate positions of the high magnification montages below. (h‐j) AMBN signal is absent in the Ambn lacZ/lacZ mouse mandibular incisor sections. (k) A second longitudinal section from Ambn lacZ/lacZ mouse showed minor autofluorescence within blood vessels in pathological areas. Similar autofluorescence was observed in this region using the amelogenin antibody (Figure 4)
