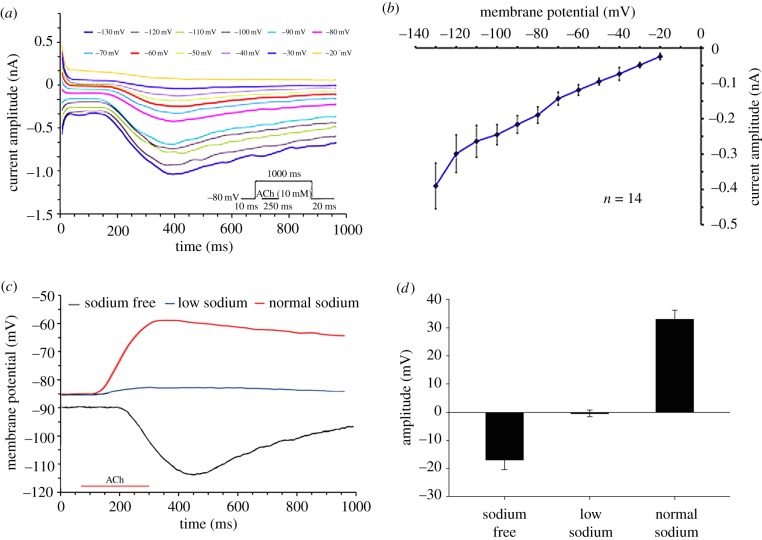
Figure 4.
Electrophysiological characterization of the ACh-induced membrane current. (a) Example of voltage-clamp experiment showing the current time course and amplitude as a function of 12 voltage step commands. Each voltage step is indicated by a different colour. (b) Voltage–current curve of the ACh-induced current (average ± s.e.m., n = 14). The current was elicited by injection of 1 mM ACh for 250 ms during 1000 ms voltage steps of 10 mV from a holding potential of −80 mV. The relationships are close to linear with extrapolated reversal potential value close to −10 mV. (c) Current-clamp experiments showing the time course of the voltage response to the application of ACh under three conditions: normal Na+ (red line), low Na+ concentration buffer (blue line), Na+-free ASW (black line). Note the minor ACh-induced depolarization in reduced Na+ concentration and the hyperpolarizing ACh-response in Na+ free solution. (d) Average ± s.e.m. of the ACh-induced maximal changes in membrane potential in the three ionic conditions is shown in (c) (Na+ free, n = 6; Low Na+, n = 5; Normal Na+, n = 34 cells). (Online version in colour.)