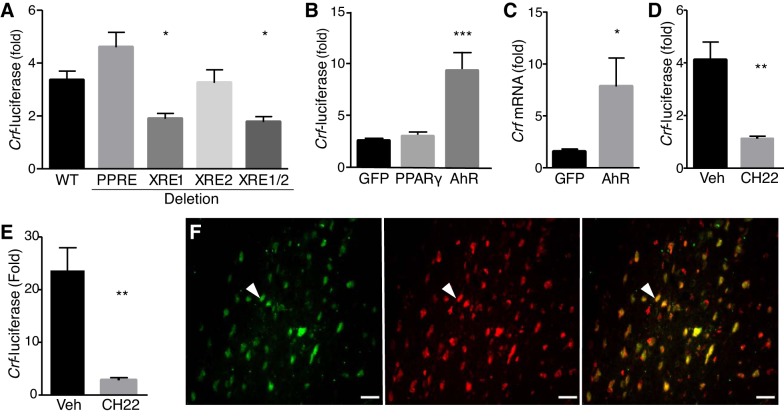
Fig. 4.
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) mediates arachidonic acid (AA)-induced corticotropin-releasing factor (Crf) expression. HEK 293T cells transfected with Crf-luciferase and stimulated with 300 µM AA. A: mutation of xenobiotic responsive element1 (XRE1) reduced AA-mediated Crf promoter activity (F = 8.884, df = 55, one-way ANOVA-Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test). B: 293T cells were also transfected with expression constructs for green fluorescent protein (GFP), peroxisome proliferator-activitor receptor-γ (PPARγ), or AhR. AA-dependent Crf expression was unaltered by PPARγ but was significantly increased by AhR (F = 15.17, df = 33, ANOVA-Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test). C: AhR overexpression in N42 cells showed increased AA-induced Crf mRNA compared with GFP when quantified by qRT-PCR and normalized to L19 (P = 0.0354, two-tailed Student’s t-test). D: in transfected 293T cells, CH-223191 inhibited AA-induced Crf-luciferase (F = 21.37, df = 6, ANOVA-Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test). E: in cultures overexpressing AhR, AA-induced Crf-luciferase is similarly inhibited by CH-223191 (F = 15.08, df = 15, ANOVA-Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test). Data are means ± SE; differences were considered statistically significant at *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. F: AhR (green) and CRF (red) immunoreactivity in brain sections of female B6 show double-labeled cells (yellow) in the paraventricular nucleus.