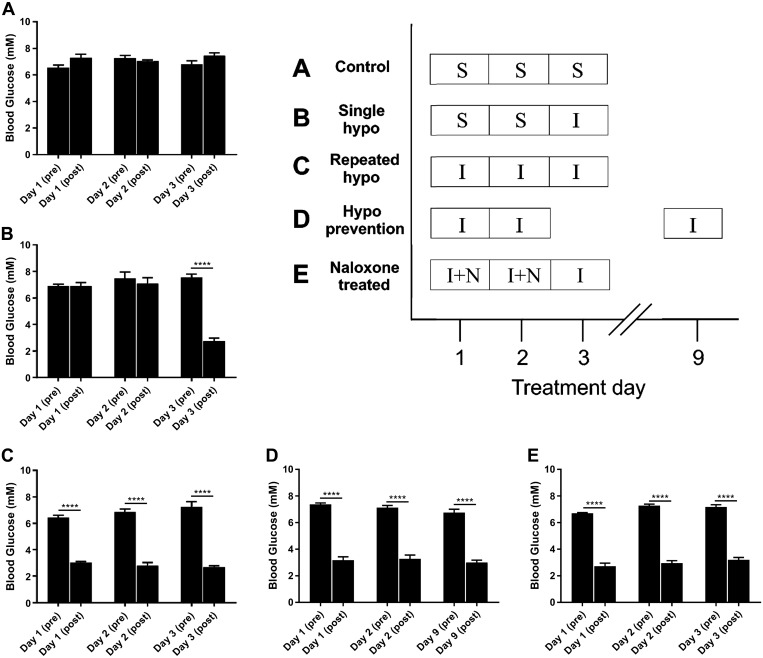
Fig. 1.
Insulin-induced hypoglycemia protocols (inset) and blood glucose levels in all treatment groups: grouped data (n = 4 animals/group) indicating blood glucose (BG) levels in groups treated with insulin (I; 5 U/kg) or saline control (S). BG levels were measured before injections and 2 h after injections. Hypoglycemia was achieved if BG ≤ 3.9 mM. In the control group (A), animals were injected with volume-matched 0.9% saline once daily for 3 days. In the single-hypoglycemia (hypo) group (B), saline was injected on days 1 and 2, followed by insulin on day 3. In the repeated-hypo group (C), insulin was injected on all days. In the hypo prevention group (D), insulin was injected on days 1, 2, and 9. In the naloxone (N)-treated group (E), insulin was injected on days 1, 2, and 3, followed by intraperitoneal injection of naloxone (1 mg/kg) after the 2-h BG levels were recorded on days 1 and 2. Data are means ± SE. Statistical significance was determined by 1-way ANOVA and multiple-comparison analysis with a Holm-Šidák correction. ****P < 0.0001, significantly different from all other groups.