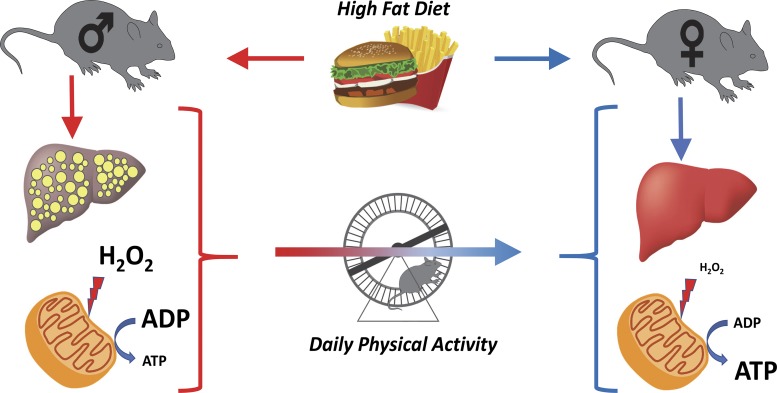
Fig. 9.
Model of hepatic response to high-fat diet (HFD) and HFD plus physical activity via voluntary wheel running (VWR) in male and female mice. Male mice are more susceptible to HFD-induced hepatic steatosis than females. This is associated with increased hepatic mitochondrial H2O2 production and reduced mitochondrial coupling and efficiency. Females are protected from HFD-induced steatosis concomitant with low hepatic mitochondrial H2O2 production and increased coupling control. The addition of VWR in male mice drives their hepatic mitochondrial phenotype toward those of females by eliciting reduced steatosis and mitochondrial H2O2 production and increasing coupling.