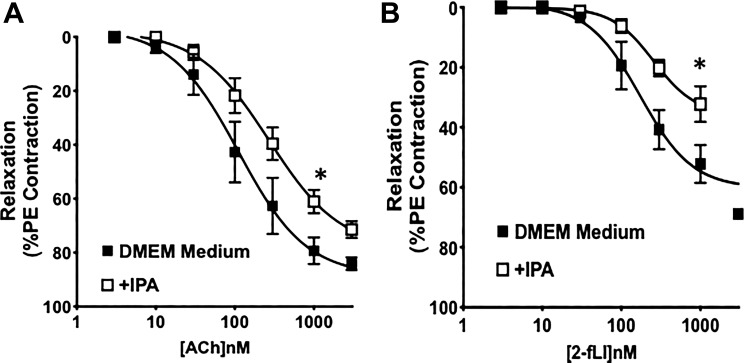
Fig. 4.
Organ culture of aorta tissues with indole 3-propionic acid (IPA) alters agonist-stimulated endothelium-mediated vasodilation. Concentration-effect curves were obtained for acetylcholine- (Ach; A) and 2-furoyl-Leu-Ile-Gly-Arg-Leu-Orn-amide (2-fLi; B)-induced vasodilation in aorta rings from pregnane X receptor (Pxr)+/+ mice cultured in in DMEM-5 mM glucose medium for 24 h in the absence or presence of 0.1 μM IPA. IPA treatment reduced the tissue sensitivity to the vasodilator actions of ACh and 2fLI (concentration-effect curves; ■) compared with their actions in untreated tissues (concentration-effect curves; □). Data points represent means ± SE (bars); n = 6 for each group. Two-way ANOVA was used for evaluating the statistical difference between concentration-response curves. *P < 0.05 for IPA-treated tissues vs. nontreated tissues.