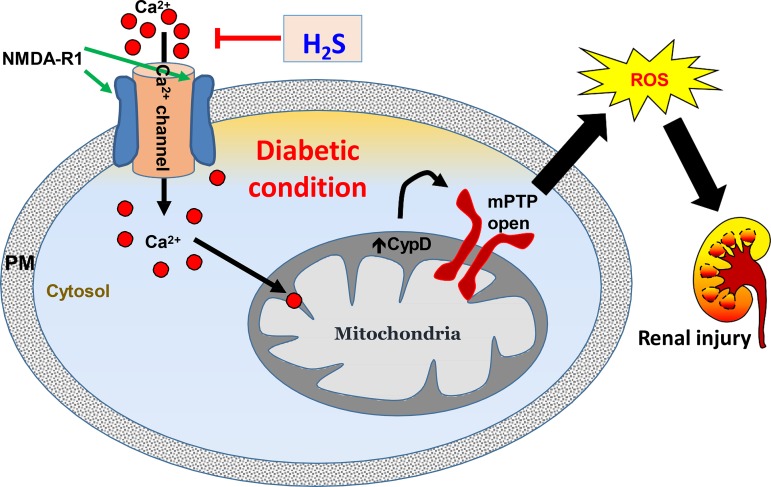
Fig. 10.
Schematic of overall findings. In diabetes, N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor 1 (NMDA-R1) mediates Ca2+ influx causing cyclophilin D (CypD) activation and mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) opening in mitochondria leading to oxidative outburst and renal endothelial injury. H2S treatment mitigates NMDA-R1 expression, possibly blocks Ca2+ channel, and thus inhibits CypD and MPTP opening and prevents renal damage. PM, plasma membrane; ROS, reactive oxygen species.