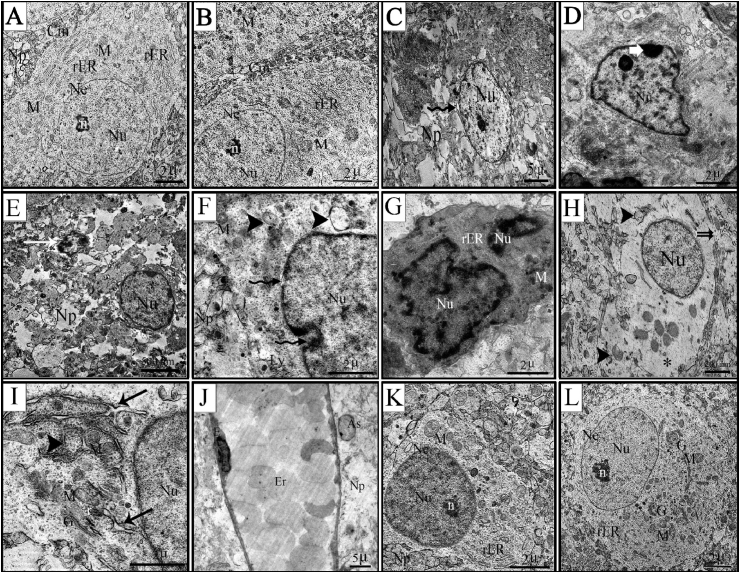
Fig. 6.
Transmission electron photomicrographs of cerebral cortex sections of rat fetuses. (A) Control group (B) Ginger group (C–J) GBP group (K&L) GBP + ginger group. A&B- perikaryons of normal nerve cell containing euchromatic nucleus (Nu) with normal nuclear envelope (Ne), and prominent nucleolus (n), normal cytoplasm containing (rER) and mitochondria (M) as well as intact cell membrane (Cm). Normal neuropil without any signs of edema (Np). C- chromatolytic nuclei (Nu) with abnormal nuclear envelop (wavy arrow) and swollen neuropil (Np). D-abnormal nuclei (Nu) with chromatin clumping below the nuclear membrane (white arrow). E-shrunken nucleus (arrow) surrounded by vacuolated neuropil (Np). F- indentation and discontinuity in the nuclear envelope (wavy arrow) accompanied by swollen mitochondria (M) with partial or total loss of cristae (arrow head) and swollen neuropil (Np), in addition to increased number of lysosomes (Ly). G-apoptotic cell with degenerated nucleus (Nu) and very electron dense cytoplasm. H- rarefied cytoplasm (*) with few scattered mitochondria, some of which were ruptured (arrow head). The discontinuity in the cell membrane was evident (double arrow). I- dilated and fragmented rER with partial loss of the attached ribosomes (arrow), swollen mitochondria with partial loss of cristae (arrow head). J-enlarged and dilated brain capillary with obvious congestion (Er). K&L-nerve cells with normal appearing nuclei (Nu) and prominent nucleoli (n). Normal cytoplasm containing mitochondria (M) and Golgi (G), although the rER appeared fragmented. Surrounding neuropil is similar to that of the control nerve cells (Np).