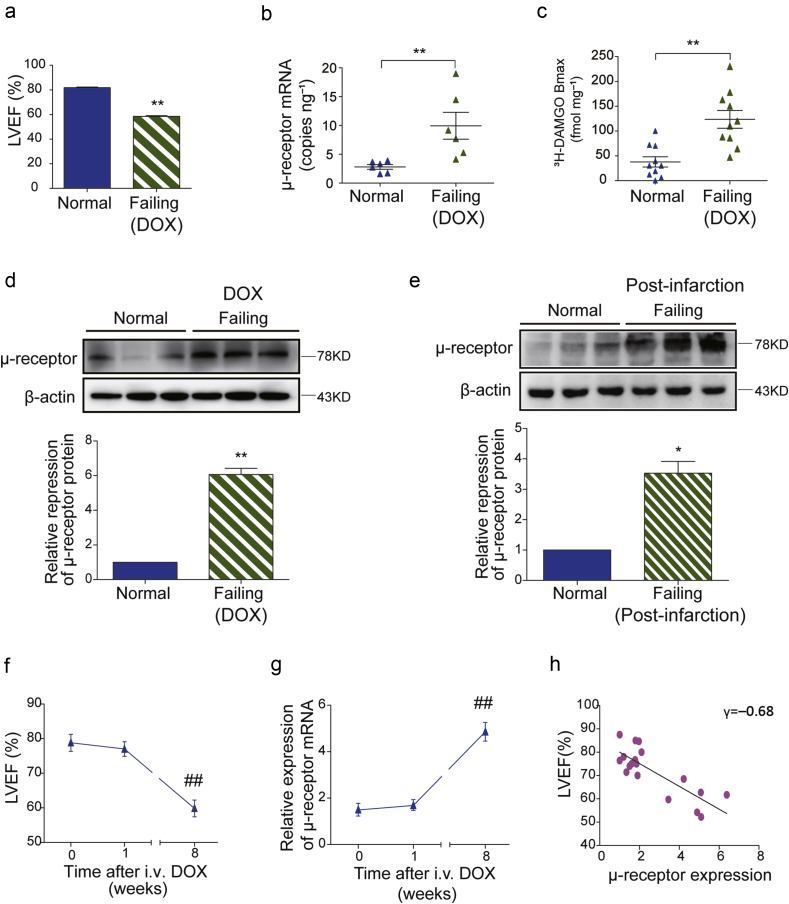
Fig 1.
Up-regulation of cardiac μ-opioid receptors in rats with heart failure. (a) Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) values of normal saline (NS, normal) or doxorubicin (DOX, failing) injected rats were measured and automatically calculated by the echocardiography system at the end of the 8th week (n=20). (b) The copy numbers of cardiac μ-opioid receptor mRNA in normal and DOX-induced failing rat heart tissues were detected by absolute quantitative RT-PCR (n=6). (c) The μ-opioid receptor specific binding capacity measured by radio-labelled specific μ-opioid receptor agonist [3H] DAMGO (n=10). (d) Representative immunoreactive bands of cardiac μ-opioid receptor protein in normal (NS) and DOX-induced failing rat heart samples. The relative expression of cardiac μ-opioid receptor protein was normalised to β-actin and the value in the normal group was assigned as 1 (n=6). (e) Representative immunoreactive bands of cardiac μ-opioid receptor protein in normal (Sham) and post-infarction failing rat heart samples. The relative expression of cardiac μ-opioid receptor protein was normalised to β-actin and the value in the normal group was assigned as 1 (n=6). *P<0.05, **P<0.01; unpaired Student's t-test. (f) LVEF was evaluated by echocardiography before (0 week), and at 1, 8 weeks after DOX injection. (g) Cardiac μ-opioid receptor mRNA concentrations were detected by relative quantitative RT-PCR at 0, 1, and 8 weeks after DOX injection. Each data point represents mean (sem) from six rats. ##P<0.01 compared with the initial data point by one-way anova followed by Tukey's test. (h) Correlational analysis of LVEF (%) and cardiac μ-opioid receptor relative expression (P<0.01 by linear regression, n=18). anova, analysis of variance; DAMGO [D-Ala,2N-MePhe,4 Gly-ol],-enkephalin; sem, standard error of the mean.