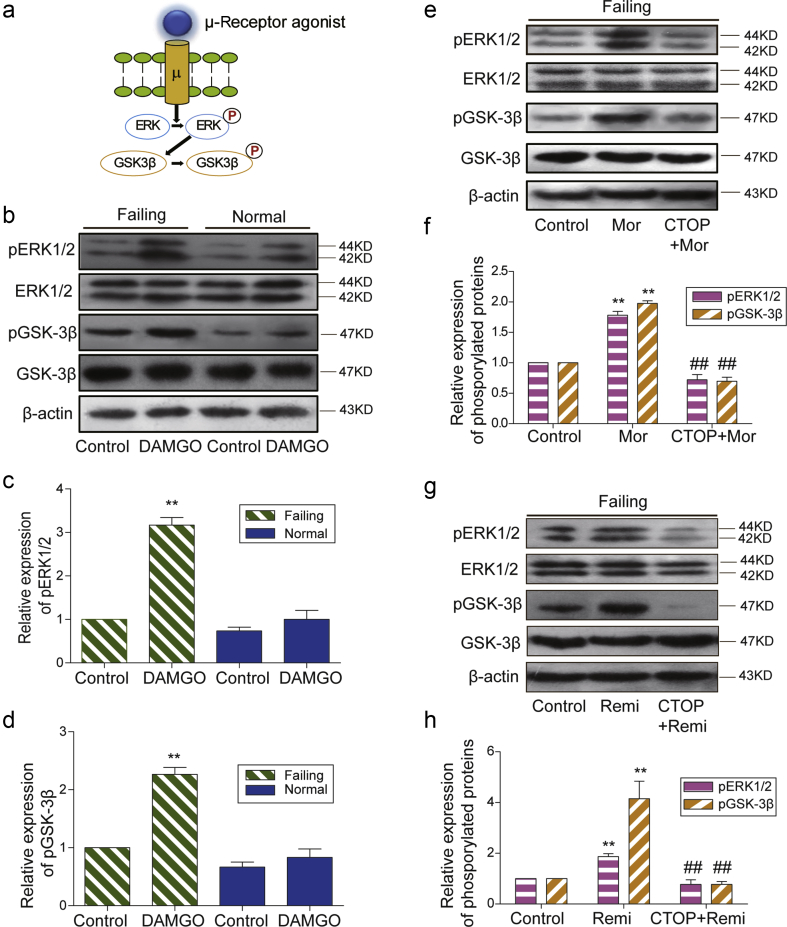
Fig 4.
μ-Opioid receptor dependent enhancement of ERK and GSK-3β phosphorylation. (a) A cartoon shows the activation of μ-opioid receptor by its agonists (DAMGO, morphine, or remifentanil) leading to phosphorylation (P) of ERK1/2 and downstream GSK-3β. (b) The μ-opioid receptor agonist DAMGO differentially induced the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and GSK-3β in failing and normal hearts. The relative expression of (c) p-ERK1/2 or (d) p-GSK-3β was normalised to total ERK1/2 or total GSK-3β and β-actin. The value in failing control group was assigned as 1. Each bar graph represents the average of mean (sem) from four rats. **P<0.01 compared with control group by two-way anova followed by Bonferroni's test. The μ-opioid receptor antagonist CTOP inhibited (e) morphine and (g) remifentanil-induced phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and GSK-3β in failing hearts. The relative expression of (f) p-ERK1/2 or (h) p-GSK-3βwas normalised to total ERK1/2 or total GSK-3β and β-actin. The value in the control group was assigned as 1. Each bar graph represents the average of mean (sem) from four rats. **P<0.01 compared with the control group, ##P<0.01 compared with morphine or remifentanil group by one-way anova followed by Tukey's test. anova, analysis of variance; P, phosphorylation; Mor, Morphine; Remi, Remifentanil; DAMGO [D-Ala,2N-MePhe,4 Gly-ol],-enkephalin; CTOP, D-Pen-Cys-Tyr-D-Trp-Orn-Thr-Pen-Thr-NH2; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; GSK3ß, glycogen synthase kinase; sem, standard error of the mean.