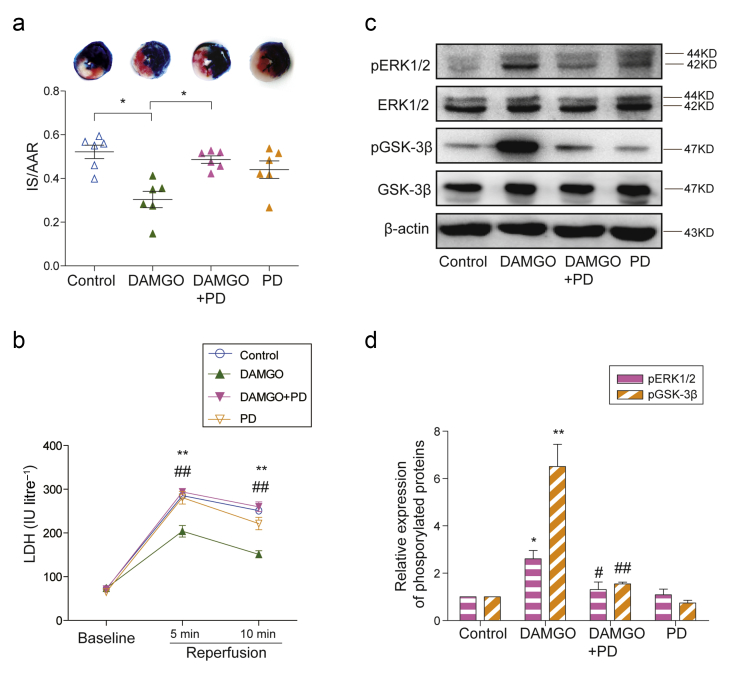
Fig 5.
ERK signalling dependent mechanism of μ-opioid receptor-induced cardioprotection. (a) The ERK inhibitor PD98059 (PD) blocked the reduction of DAMGO on infarct size/area at risk (IS/AAR) in isolated failing hearts (n=6, *P<0.05, one-way anova followed by Tukey's test). (b) The coronary effluents from isolated failing hearts were collected at baseline, 5 min, and 10 min after reperfusion to measure the activity of LDH. Each data point represents the average of mean (sem) from six rats. **P<0.01 compared with control group, ## P<0.01 compared with DAMGO group by two-way repeated anova followed by Bonferroni's test. (c) The ERK inhibitor PD98059 suppressed DAMGO-induced phosphorylation levels of ERK1/2 and GSK-3β in failing hearts. (d) The relative expression of p-ERK1/2 or p-GSK-3β was normalised to total ERK1/2 or total GSK-3β and β-actin. The value in control group was assigned as 1. Each bar graph represents the average of mean (sem) from four rats. **P<0.01, *P<0.05 compared with control group, ##P<0.01, #P<0.05 compared with DAMGO group by one-way anova followed by Tukey's test. anova, analysis of variance; DAMGO [D-Ala,2N-MePhe,4 Gly-ol],-enkephalin; PD, PD98059; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; GSK3ß, glycogen synthase kinase; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; sem, standard error of the mean.