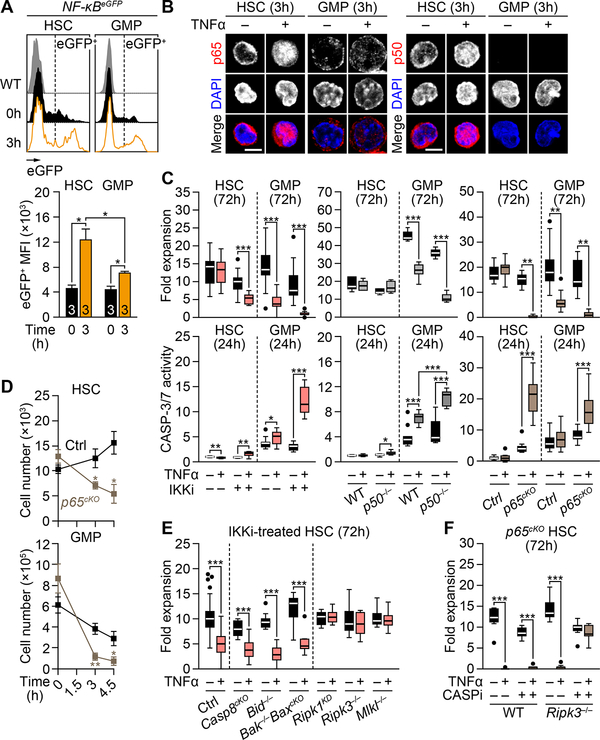
Figure 3. TNFα-mediated p65/NF-κB activation protects HSCs from necroptosis.
(A) NF-κB activity in BM NF-κB-eGFP HSCs and GMPs 3h post-TNFα injection (n = 3 mice/group from 2 independent experiments). Results are shown as eGFP MFI levels in the corresponding gates.
(B) p65 and p50 localization in BM HSCs and GMPs after 3h culture ± TNFα; scale bars, 5 μm.
(C) NF-κB inhibition due to IKK inhibitor (IKKi, 2 μM BMS-345541; left), p50 deficiency (p50−/− mice; middle) or p65 deficiency (p65cKO mice; right) on 72h expansion (n =6–15 pools of 300 cells/group from 3–5 independent experiments, top) and 24h CASP-3/7 activity (n = 9–15 pools of 200 cells/group from 3–4 independent experiments, bottom) in BM HSCs and GMPs cultured ± TNFα. Results are expressed as fold expansion compared to the number of plated cells/condition (top), or fold changes compared to untreated WT or Ctrl HSCs (set to 1, bottom).
(D) Absolute numbers of BM HSCs and GMPs in Ctrl and p65cKO mice ± TNFα (n = 3–5 mice/group from 5 independent experiments; * vs. Ctrl).
(E) Expansion of the indicated IKKi-treated BM HSCs after 72h culture ± TNFα (n = 9–63 pools of 300–500 cells/group from 21 independent experiments). Results are expressed as fold expansion compared to the number of plated cells/condition.
(F) Expansion of the indicated BM HSCs after 72h culture ± TNFα and pan-caspase inhibitor (CASPi, 20 μM zVAD-fmk) (n = 8–9 pools of 300 cells/group from 3 independent experiments). Results are expressed as fold expansion compared to the number of plated cells/condition.
Data are mean ± SEM, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
See also Figure S3.