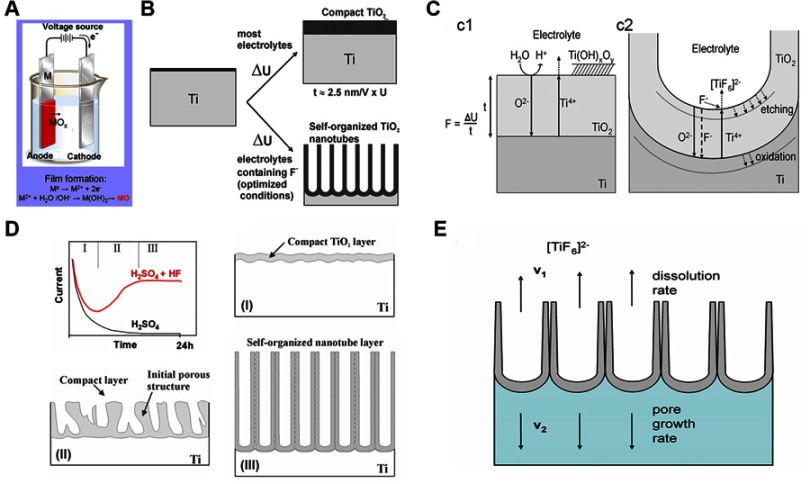
Figure 2.
Anodization process of TNTs.24
Note: (A) Schematic diagram of the anodizing apparatus. (B) Formation of compact or nanoporous (nanotube) titanium dioxide layers depending on anodizing parameters. (C) Schematic representation of Ti anodization (c1) without fluorides and (c2) with fluorides. (D) Characteristic current transients during anodization with or without fluorides in the electrolyte and variation of TNT morphology in the three reaction stages. (E) Equilibrium growth situation with equal rates of titanium dioxide dissolution (v1) and formation (v2). Reprinted from Curr Opin Solid St M, 11(1-2), Macak JM, Tsuchiya H, Ghicov A, et al, TiO2 nanotubes: Self-organized electrochemical formation, properties and applications, 3-18, Copyright (2007) with permission from Elsevier.
Abbreviation: TNT, titanium dioxide nanotube.