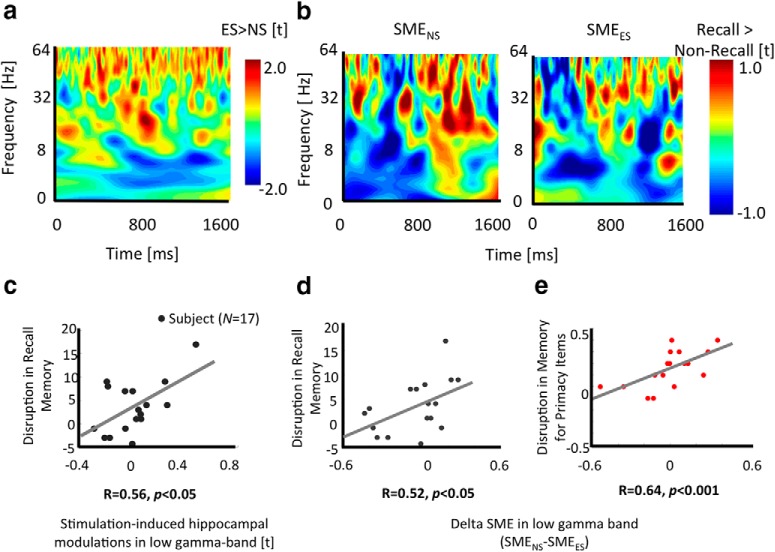
Figure 3.
Stimulation induces changes in low gamma and theta band oscillations in the hippocampus and neural changes are linked to behavioral memory disruptions. a, Frequency–time plot of a sample participant showing increases in low and high gamma band power and decrease in theta band power during ES versus NS conditions. b, Frequency–time plot of a sample participant showing power differences when an item is successfully recalled versus forgotten (successful memory effect, SME) in ES (left) and NS (right) conditions. Gamma power increased whereas theta power decreased in both cases. For a, b: Y-axis represents frequency [Hz]; X-axis represents time [ms]. c, Significant positive correlation between stimulation induced hippocampal gamma power changes (measured as t-statistics of the contrast between ES versus NS conditions) and disruption in the memory (measured as percentage recall during NS minus ES conditions). In d and e, there was a significant positive correlation between delta hippocampal gamma SME (measured as follows: SME in NS minus SME in ES condition) and disruption in memory performance (measured as follows: percentage recall of all items/percentage recall of primacy items in NS minus that in ES condition).