Figure 4.
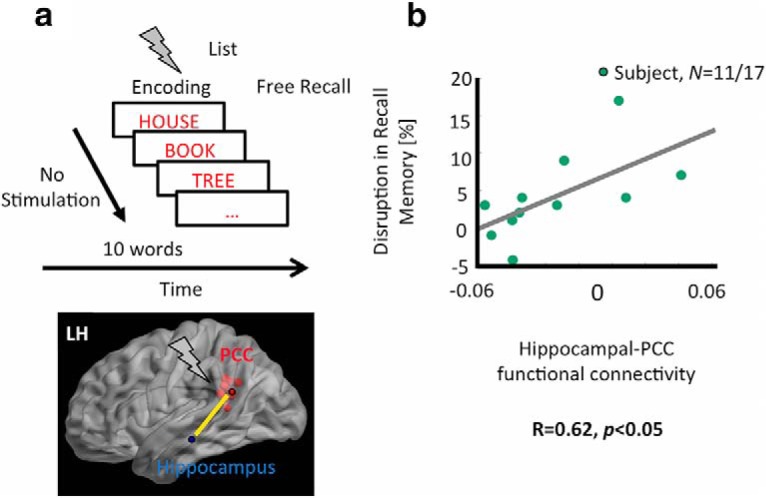
Baseline PCC–hippocampal functional connectivity is positively linked to stimulation-induced memory disruptions. a, PCC–Hippocampal functional connectivity, measured as oscillatory synchrony between hippocampal electrodes and PCC electrodes (in a subset of participants, n = 11 of 17) in a second free recall experiment in the absence of stimulation. b, Positive correlation between baseline functional connectivity and stimulation-induced recall memory disruption. That is, participants with higher PCC–hippocampal functional connectivity tended to show a larger disruption in memory performance due to stimulation.
