Figure 6.
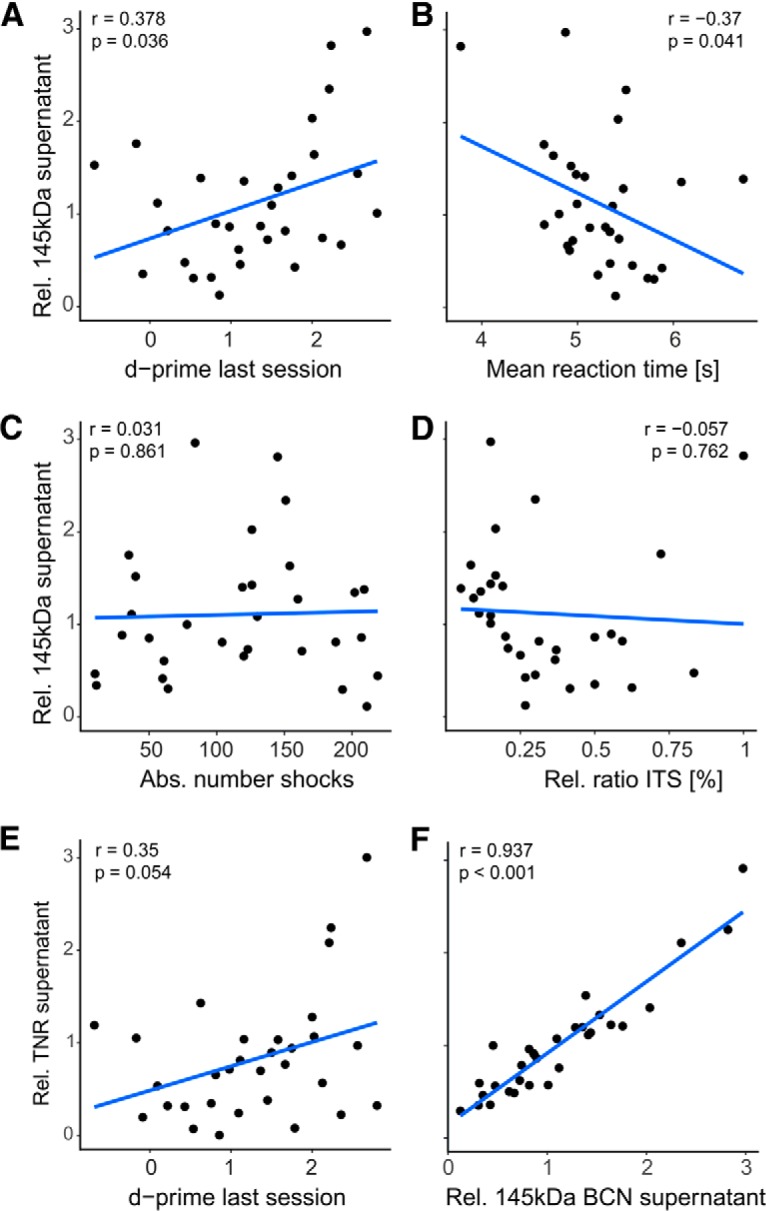
Correlation analysis of behavioral parameters and biochemical modulation of the 145 kDa BCN fragment in the supernatant fraction. Data were taken from training groups AV, AQ, RT, and LP. A, Relative abundance of 145 kDa BCN in the supernatant fraction was positively correlated with the d′ value in the last training session indicating its performance dependent upregulation. B, The corresponding correlation between 145 kDa BCN and reaction times was significantly negative. In contrast, no significant correlation was found between supernatant 145 kDa BCN and absolute number of shocks (C) or the ratio of relative intertrial shuttles (D). E, Relative abundance of TNR in the supernatant fraction showed a trend of a positive correlation with the d′ value in the last training session (p = 0.054). Hence, this trend is in line with the performance-dependent upregulation of 145 BCN in A. F, Furthermore, Pearson correlation of the both full-length proteins TNR and 145 kDa BCN in the supernatant fraction were highly correlated. This implies a close interaction of the two ECM full-length proteins in the supernatant fraction and their differential regulation in the loose and cell-bound/PNN-associated ECM.
