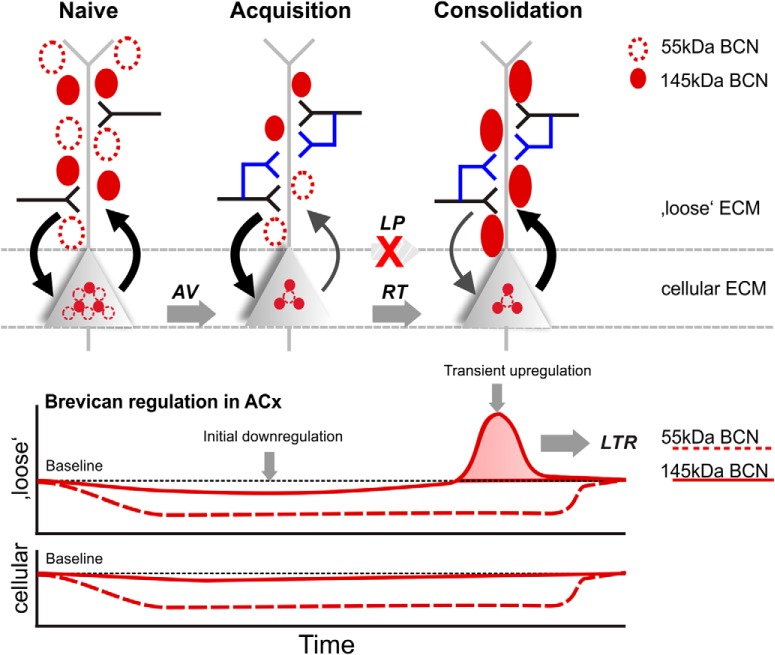
Figure 8.
Learning-dependent regulation of BCN in auditory cortex. During acquisition of learning an initial downregulation of BCN in both, the cellular and loose ECM fraction (bottom) is permissive for learning-dependent synaptic remodeling (top). The cellular ECM here refers to the cell-bound and PNN-associated forms of the ECM, as extracted in the cellular fraction (pellet) of auditory cortex samples (Deepa et al., 2006). Here, new synaptic contacts are established during acquisition learning. Note that such downregulation was not present in the non-associative control group (Fig. 5), and hence, the downregulation is specific for early associative training. During consolidation of recent memories, a transient upregulation of the supernatant 145 kDa full-length BCN (bottom) is obstructive for further structural plasticity. During this RT phase, recent memories are resistant against remodeling (Happel et al., 2014). This transient protection of recently acquired memories might be fundamental for their remote recall, as this was not found in LP animals. During LTR, levels of both BCN fragments returned to baseline, as no new (re-)learning is initiated.