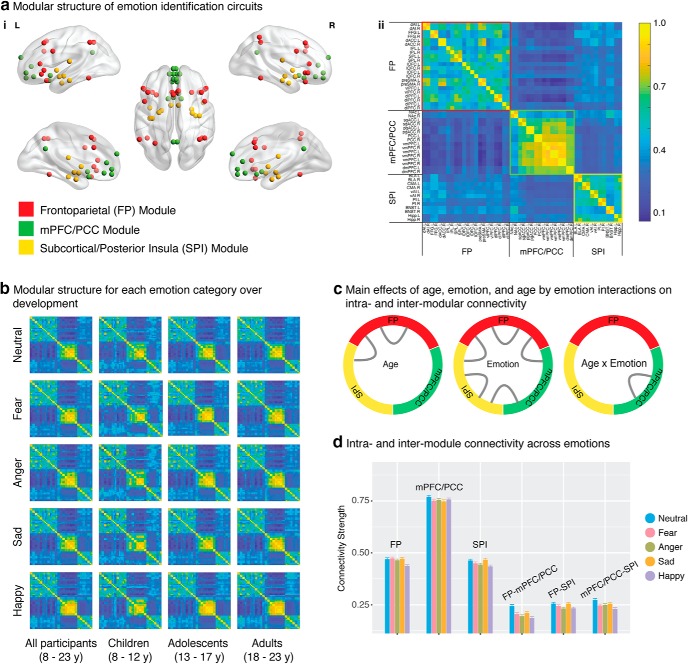
Figure 3.
Main effects of age and emotion on modular organization and connectivity. ai, Three functional modules were identified across all participants: the FP module (red), mPFC/PCC module (green), and SPI module (yellow). aii, As shown in the group consistency matrix, the FP module (red border) includes bilateral dlPFC, vlPFC, dACC, pre-SMA, IPL, SPL, and FFG. The mPFC/PCC module (blue border) includes bilateral NAc, sgACC, pgACC, PCC, vmPFC, and dmPFC. The SPI module (yellow border) includes BLA, CMA, vAI, PI, BNST, and hippocampus (Hipp). Color bar represents the probability of two nodes being classified in the same module across participants. b, As shown in the group consistency matrices, overall modular structure is stable across all five emotion categories and age groups (children 8–12 years, adolescents 13–17 years, adults 18–23 years). c, Intra-FP connectivity and FP-SPI connectivity increased with age; intra-FP, intra-SPI, and all intermodule connectivity measures varied across emotions; age-related changes in intra-mPFC/PCC connectivity were modulated by emotion category. d, Intramodule and intermodule connectivity varied across emotions. Data are mean ± SEM.