Figure 7.
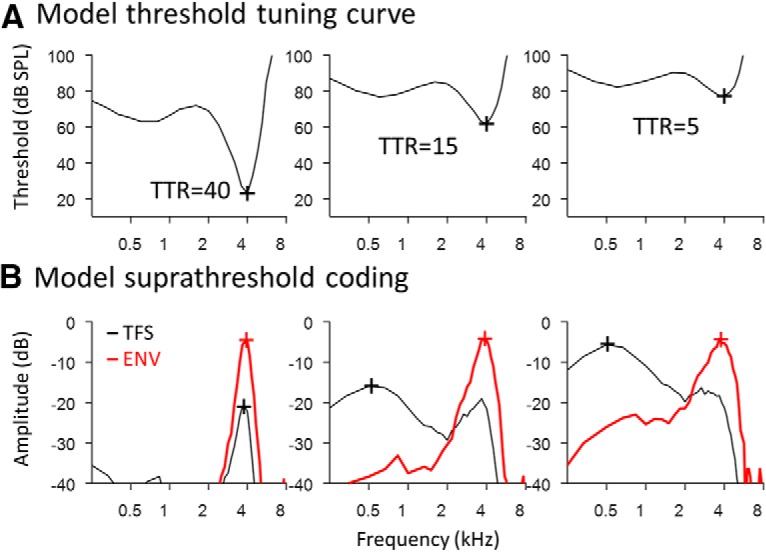
Predicted relationship between TTR of cochlear frequency tuning and suprathreshold AN encoding of broadband sound. A, The model consists of a band-pass filter with tip and tail components, followed by half-wave rectification and low-pass filtering to capture the roll-off of AN phase locking with increasing frequency. B, Suprathreshold coding of TFS and ENV, quantified using Wiener–kernel analyses of model responses to broadband noise. Lower TTR of cochlear frequency tuning is associated with increased coding of low-frequency stimulus component and greater coding deficits for TFS than ENV, as observed physiologically. Note that the roll-off of AN phase locking remained unchanged in the model, suggesting that effects of NIHL/MHL on AN temporal coding result from changes in the TTR of cochlear frequency tuning, rather than an explicit deficit in the fundamental phase-locking ability of AN fibers.
