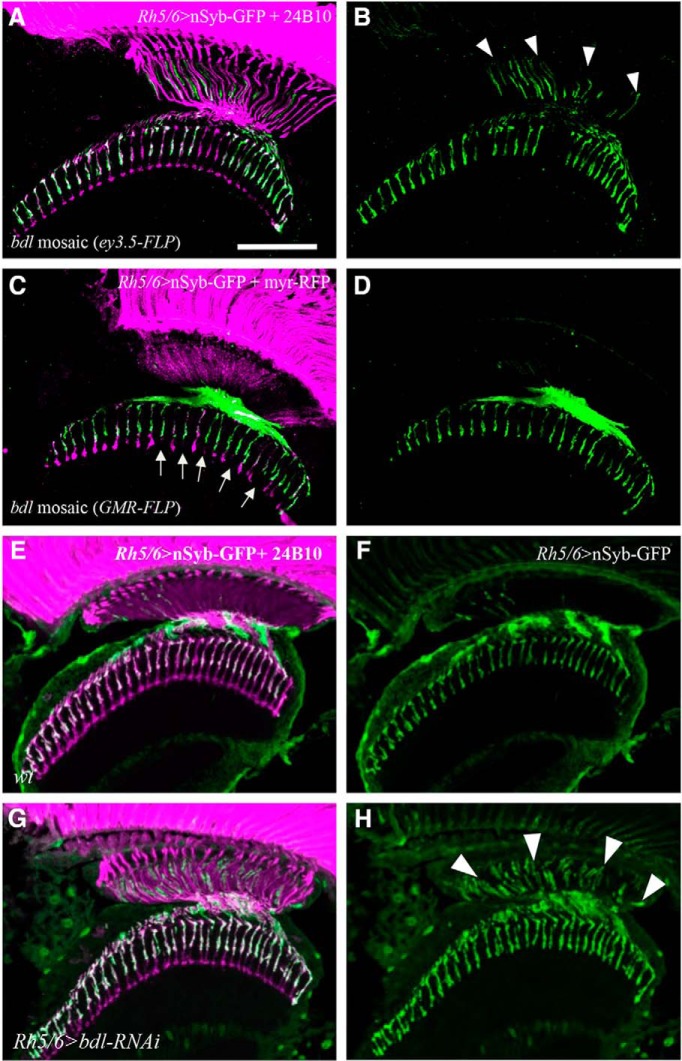
Figure 2.
bdl is required cell-autonomously in R8 axons. A, B, Frozen sections of adult heads were stained with anti-GFP (green) and MAb24B10 (magenta). A, In all eye-specific bdl mosaic animals examined (100%, n = 6 animals), strong nSyb-GFP staining was observed in the proximal portion of bdl mutant R8 axons. B, The section in A was visualized with nSyb-GFP staining only. Arrowheads indicate proximal portions of R8 axons with mislocalized nSyb-GFP. C, D, Frozen sections of adult heads were stained with anti-GFP (green) and anti-RFP (magenta). Homozygous bdl mutant R7 axons were generated by GMR-FLP-induced mitotic recombination. C, In all GMR-FLP-induced bdl mosaic animals examined (100%, n = 6 animals), nSyb-GFP staining (green) was still predominantly localized to R8 axonal terminals in the medulla. Wild-type or heterozygous R-cell axons were labeled with GMR-myr-mRFP (magenta). Mosaic columns were identified by the absence of RFP staining in bdl mutant R7 axons (arrows). D, The section in C was visualized with nSyb-GFP staining only. E, In wild-type double-stained with anti-GFP (green) and MAb24B10 (magenta), nSyb-GFP staining was predominantly localized to R8 axonal terminals in the medulla (100%, n = 5 animals). F, The section in E was visualized with nSyb-GFP staining only. G, In flies expressing a UAS-bdl-RNAi transgene under control of the R8-specific driver Rh5/6-GAL4, strong nSyb-GFP staining was also observed in the proximal portion of R8 axons in the lamina (5 of 6 animals). H, The section in G was visualized with nSyb-GFP staining only. Arrowheads indicate proximal portions of R8 axons with mislocalized nSyb-GFP. Scale bar, 20 μm.