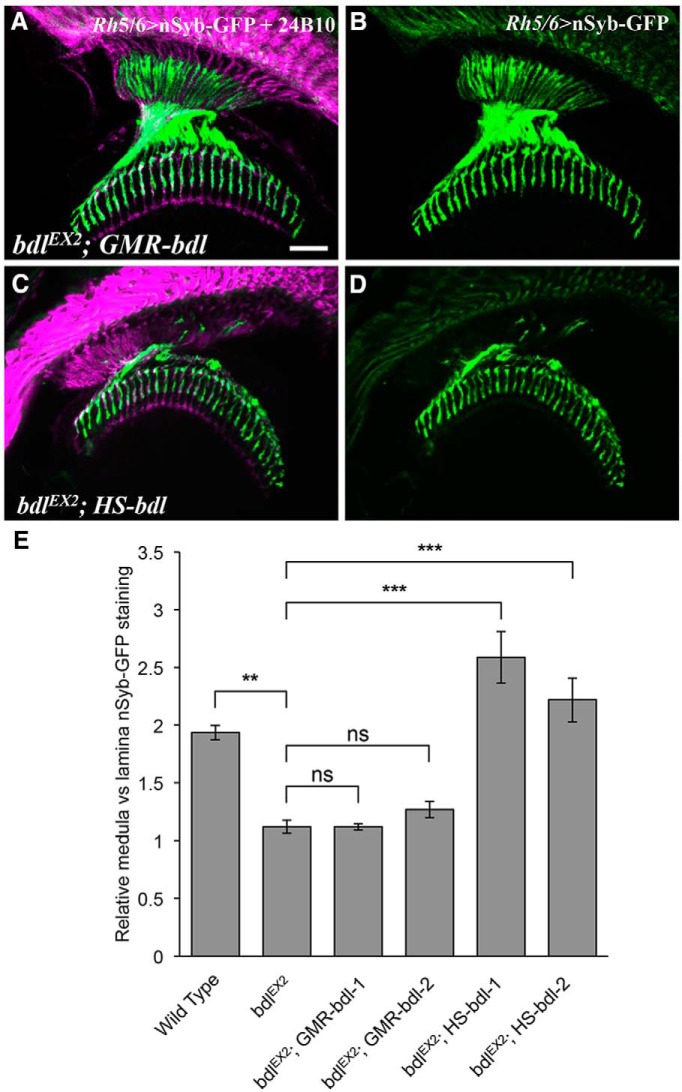
Figure 3.
Expression of bdl in R-cell axons was not sufficient for rescuing the SV phenotype in bdl mutants. A–D, Frozen sections of adult heads expressing nSyb-GFP under control of the R8-specific driver Rh5/6-GAL4, were stained with anti-GFP (green) and MAb24B10 (magenta). A, Restoring bdl expression in all R-cell axons under control of the eye-specific GMR promoter did not rescue the SV phenotype, as many SV components were still mislocalized to the proximal portion of R8 axons in the lamina. Genotype: bdlEX2; GMR-bdl/ Rh5/6-GAL4, UAS-nSyb-GFP. Two independent GMR-bdl transgenic lines were used in the experiments. Eight individuals were examined in each experiment. B, The section in A was visualized with nSyb-GFP staining only. C, Restoring bdl expression in both R-cell axons and the optic lobe under control of the heat-inducible promoter completely rescued the SV phenotype. Genotype: bdlEX2; HS-bdl/ Rh5/6-GAL4, UAS-nSyb-GFP. Two independent HS-bdl transgenic lines were used in the experiments. At least five individuals were examined in each experiment. D, The section in C was visualized with nSyb-GFP staining only. E, The ratio of medulla versus lamina relative nSyb-GFP staining intensities was quantified. One-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Tukey's test. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; ns, p > 0.05. Error bars indicate SEM. Scale bar, 20 μm.