Figure 5.
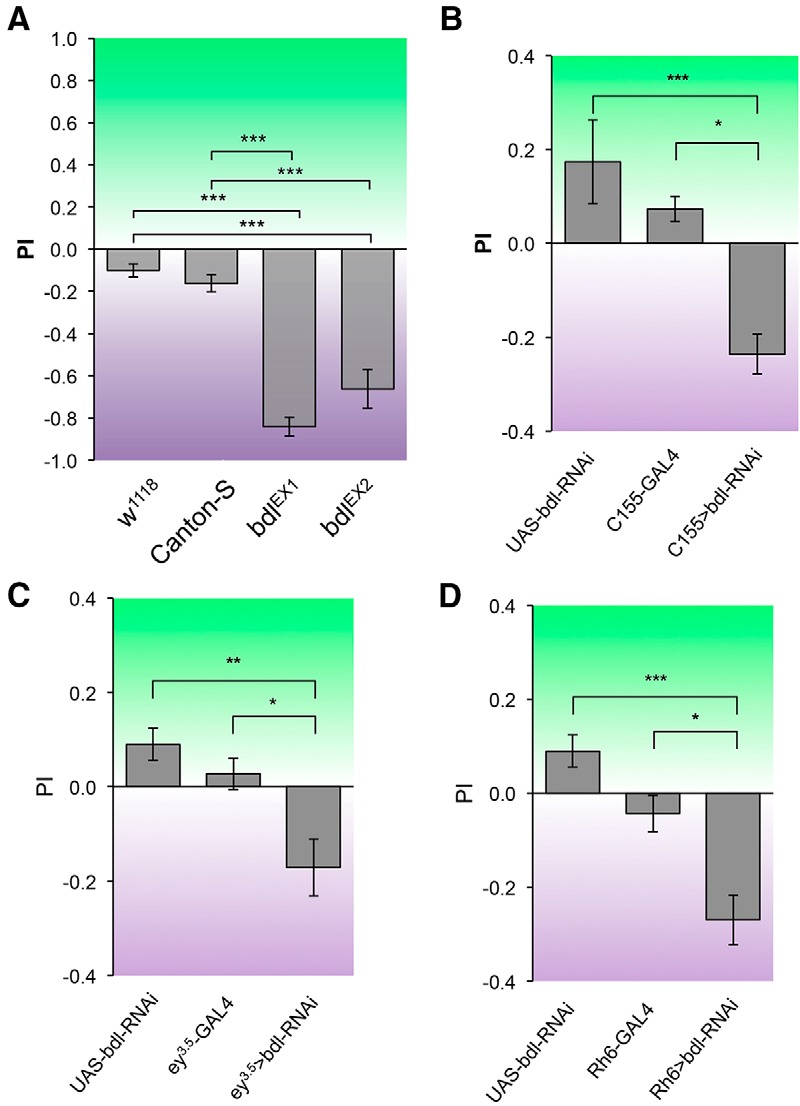
R8-dependent phototaxis response was disrupted in bdl mutants. Flies were given UV vs green choice. Light PI was calculated as described in Materials and Methods. A, Canton-S wild-type and w1118 flies could be attracted to both UV and green light sources. However, both bdlEX1 and bdlEX2 homozygous mutant flies were predominantly attracted toward UV light source. B, bdl was knocked down in flies carrying a pan-neuronal-specific driver C155-GAL4 and a UAS-bdl-RNAi transgene. Compared with control flies that carried C155-GAL4 or UAS-bdl-RNAi only, flies carrying both C155-GAL4 and UAS-bdl-RNAi showed a much greater preference for UV light. C, Eye-specific knockdown of bdl was performed by expressing UAS-bdl-RNAi under control of the eye-specific driver ey3.5-GAL4. Reducing bdl in the eye significantly decreased the preference for green light. D, bdl was specifically knocked down in green-sensitive R8 photoreceptors (i.e., R8y) by expressing UAS-bdl-RNAi under control of the R8y-specific driver Rh6-GAL4. Knocking down bdl in green-sensitive R8 decreased the preference for green light. For each genotype, ∼5–10 trials were performed, and ∼50 flies were tested in each trial. One-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Tukey's test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Error bars indicate SEM.
