Figure 6.
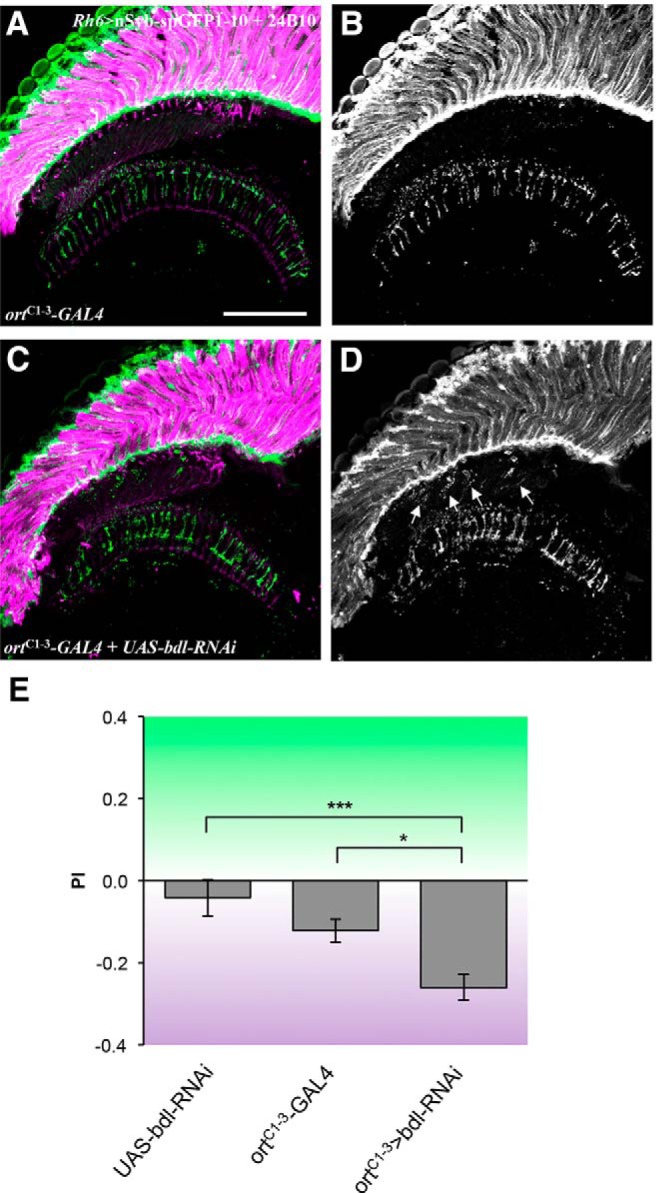
Knockdown of bdl in postsynaptic target neurons in the optic lobe disrupted the transport of SVs in R8 axons and R8-dependent phototaxis response. A–D, Frozen sections of adult heads expressing the SV marker lexAop-nSyb-spGFP1–10 under control of the green-sensitive-R8-specific driver Rh6-lexA::p65, were stained with anti-GFP (green) and MAb24B10 (magenta). A, In most control animals carrying ortC1–3-GAL4 only (6 of 7 animals), SVs labeled with nSyb-spGFP1–10 were predominantly localized to R8 axonal terminals in the medulla region. B, The section in A was visualized with nSyb-spGFP1–10 staining only. C, When bdl was knocked down in postsynaptic target neurons in the optic lobe by expressing UAS-bdl-RNAi under control of the ortC1–3-GAL4 driver, strong nSyb-spGFP1–10 staining was also observed in the proximal portion of R8 axons in the lamina (100%, n = 4 animals). D, The section in C was visualized with nSyb-spGFP1–10 staining only. Arrowheads indicate proximal portions of R8 axons with mislocalized nSyb-spGFP1–10. E, Flies were given UV vs green choice. Knocking down bdl in postsynaptic targets of R8 by expressing UAS-bdl-RNAi under control of ortC1–3-GAL4, significantly decreased the preference for green light. For each genotype, ∼10–13 trials were performed, and ∼50 flies were tested in each trial. One-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Tukey's test. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001. Error bars indicate SEM. Scale bar, 20 μm.
