Fig. 6. Hydrophobic interaction and hydrogen bonding analyses of the SULT2B1b cSNPs.
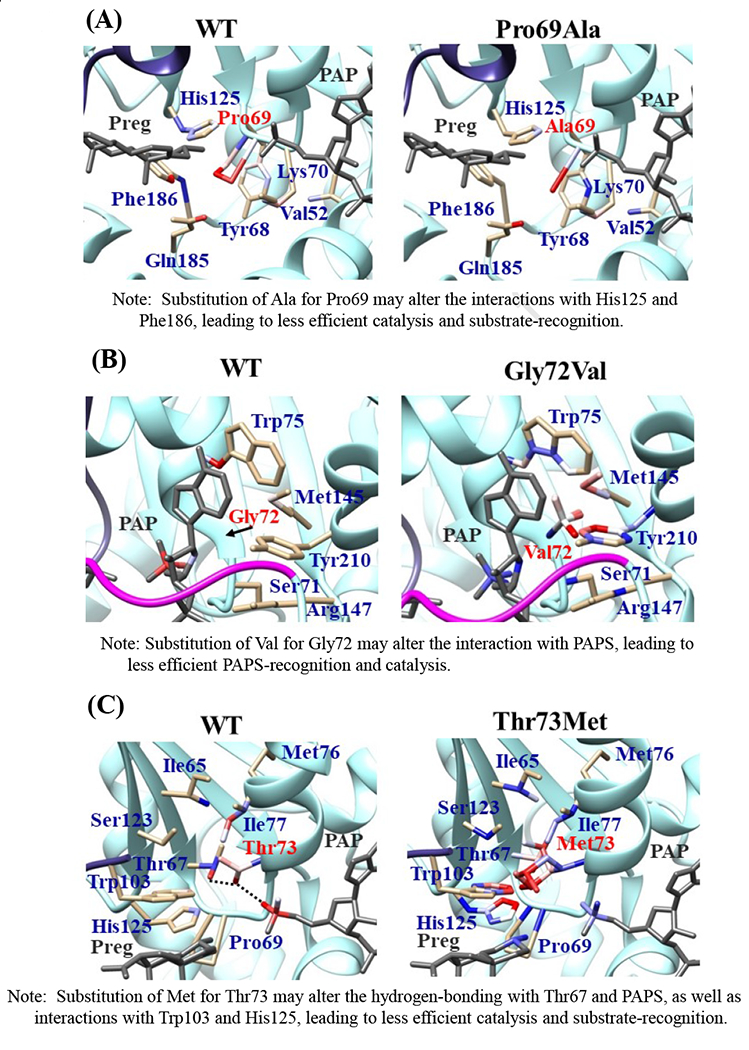
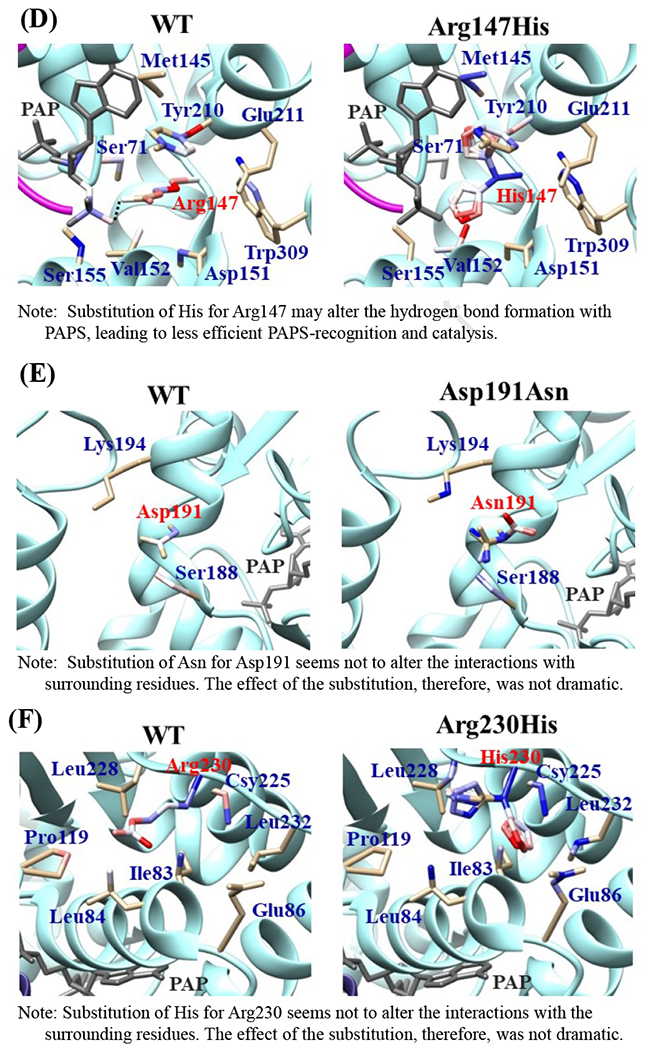
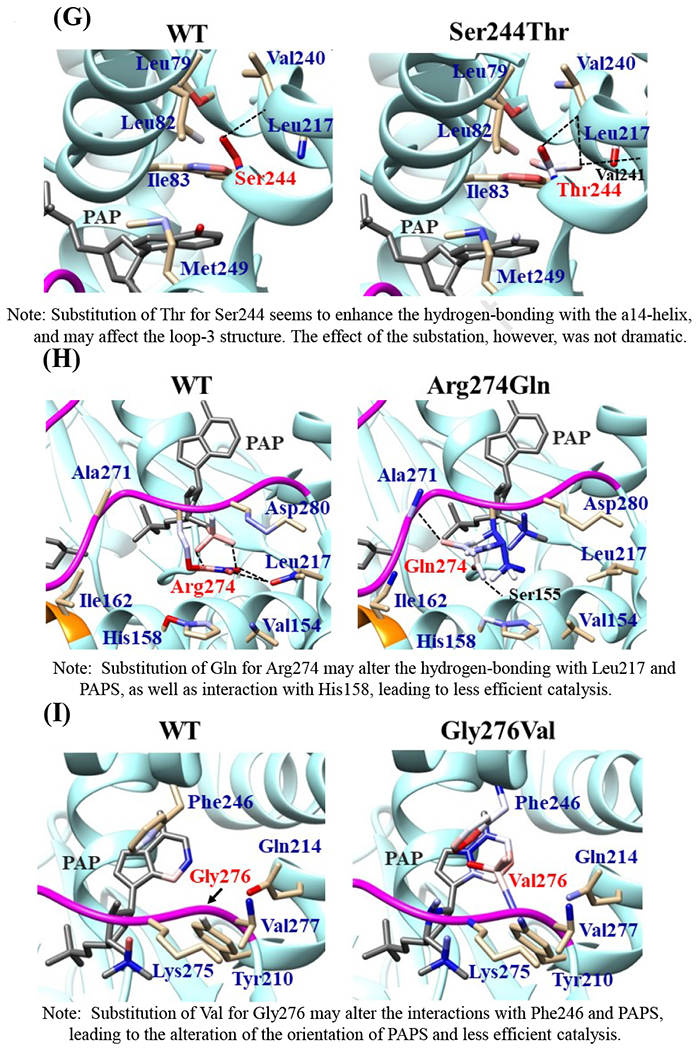
Atoms interacting with Pro69 (A), Gly72 (B), Thr73 (C), Arg147 (D), Asp191 (E), Arg230 (F), Ser244 (G), Arg274 (H), and Gly276 (I) are colored by the blue-white-red gradient (left panels). Estimated interaction formed with Ala69 in Pro69Ala (A), Val72 in Gly72Val (B), Met73 in Thr73Met (C), His147 in Arg147His (D), Asn191 in Asp191Asn (E), His230 in Arg230His (F), Thr244 in Ser244Thr (G), and Gln274 in Arg274Gln (H), Val276 in Gly276Val (I) are colored by the blue-white-red gradient (right panels). Top five-ranked rotamers of each substituted residue are modeled using the Dunbrack backbone-dependent rotamer library [Dunbrack 2002] and interaction was analyzed by Find Clashes/Contacts tool in a molecular modeling software, USCF Chimera software (Pettersen et al. 2004). Hydrogen bonds formed with Thr73 (C), Arg147 (D), Ser244 (E), and Arg274 (H) are shown by dashed lines (left panels). Estimated hydrogen bonds formed with Thr244 in Ser244Thr (G), Gln274 in Arg274Gln (H) are shown by dashed lines (right panels).
