Figure 4: EET analog alleviates I/R-induced renal epithelial cell death and intrarenal inflammation.
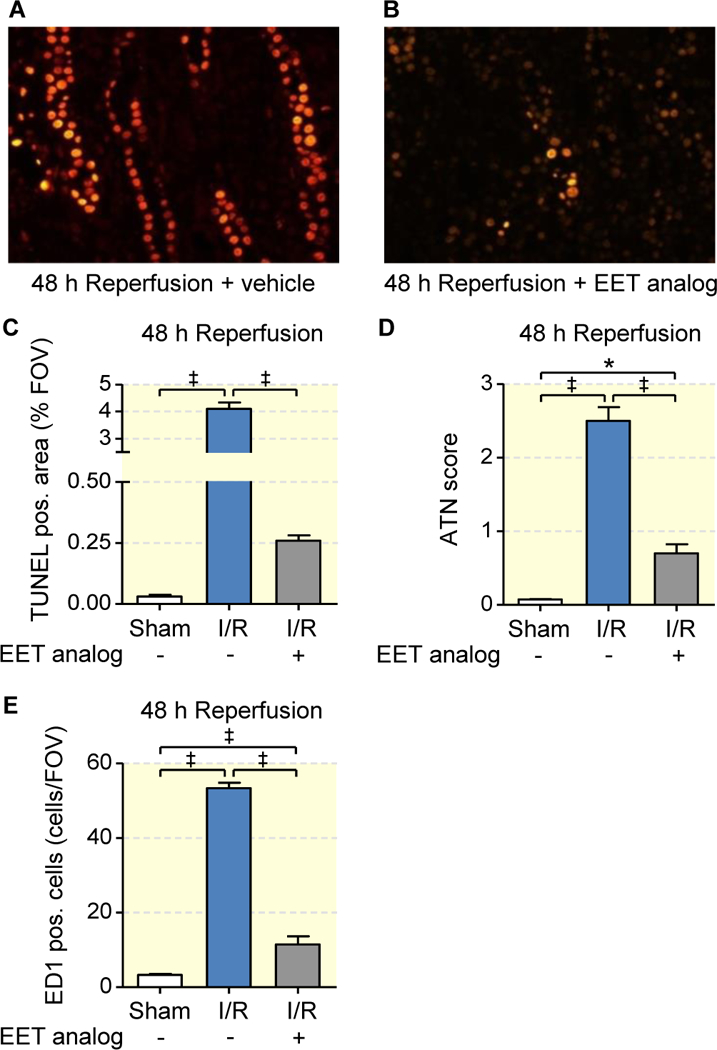
Representative images of outer medullary sections stained by TUNEL assay (a, b) with corresponding quantitative evaluation (c), and semiquantitative acute tubular necrosis score (ATN) (d) show that EET analog treatment significantly attenuates I/R induced abundant epithelial apoptosis and necrosis 48 hours after I/R as observed upon vehicle treatment. Quantification of monocyte/macrophage cell infiltration (ED1-positive cells/FOV) in the outer medulla (e) shows minimal ED1-positive cell infiltration upon EET analog treatment in comparison to vehicle at 48 hours after I/R injury. Data are given as mean ± SEM (n = 4–6 per group). Statistically significant difference were observed as indicated: *(p<0.05) and ‡(p<0.001).
