Figure 1.
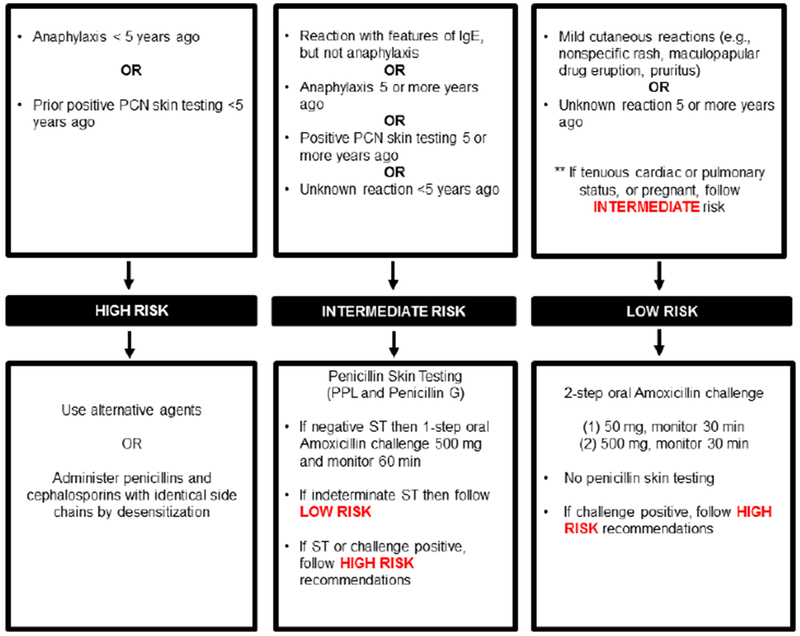
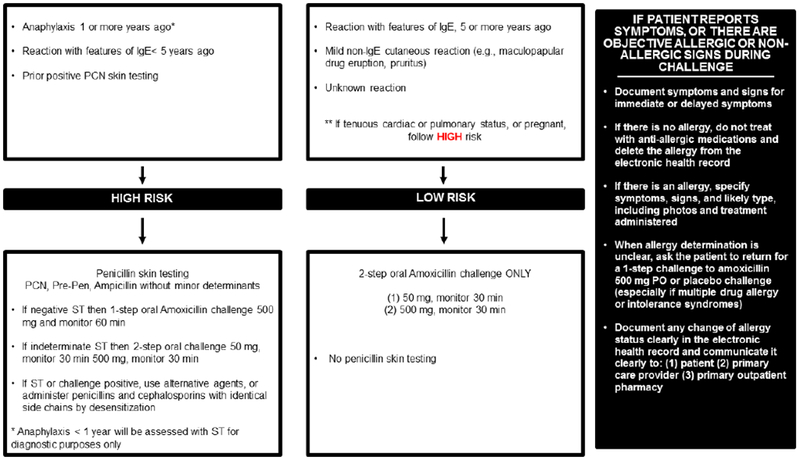
Risk-based pathway for outpatient penicillin allergy evaluations
This penicillin allergy pathway was implemented by allergists, allergy trainees, and an allergy nurse practitioner in 2017 at Massachusetts General Hospital (A). This penicillin allergy pathway was implemented in 2019 at Massachusetts General Hospital (B)
The figures demonstrate the evaluation recommended for all patients presenting for penicillin allergy evaluation whose reaction was possibly IgE-mediated. This clinical pathway does not apply to patients who have a history of a severe cutaneous adverse reaction (such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, drug-induced exfoliative dermatitis, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, or acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis), vasculitis, interstitial nephritis, or hemolytic anemia. Features of IgE included urticaria, angioedema, wheezing/bronchospasm/shortness of breath, and anaphylaxis. Anaphylaxis was defined as reactions that involve two organ systems, or hypotension/arrhythmias.
Abbreviations: PCN, penicillin; IgE, immunoglobulin E; PPL, penicilloyl-polylysine; ST, skin test
