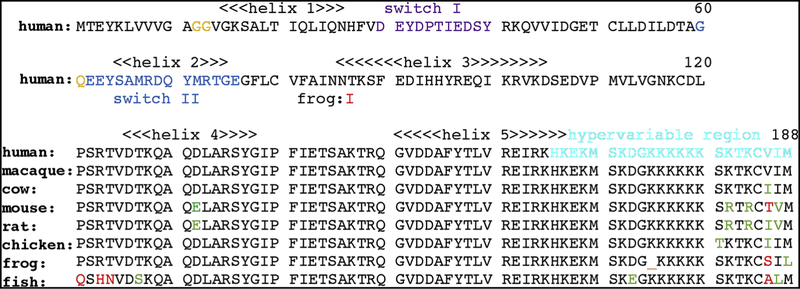
Figure 1. Alignment of KRAS4B sequences.
Shown is the coded proteins sequence of human KRAS4B (NCBI sequence ID: NP_004976.2) with helices 1–5 as indicated, switches I and II respectively colored in purple and blue, residues associated with activating mutations in gold, and the hypervariable region (HVR) in cyan. Note that the KRAS4B HVR is post-translationally processed by farnesylation at cysteine 185, proteolytic removal of residues 186–188, and carboxymethylation of the farnesylated C-terminal cysteine. Note also that residues 1–120 of human KRAS4B are identical to macaque (Macaca mulatta; NP_00124844.1), cow (Bos taurus; NP_001103471.1), mouse (Mus musculus; NP_067259.4), rat (Rattus norvegicus; NP_113703.1), chicken (Gallus gallus; NP_001243091.1), frog (Xenopus laevis; XP_01811022.1) and zebra fish (Danio rerio; NP_001003744.1) residues 1–120 except for the indicated frog residue 87. Sequence variations among the shown vertebrate KRAS4B proteins through residues 121–188 are indicated in green for conservative changes and red for non-conservative replacements.