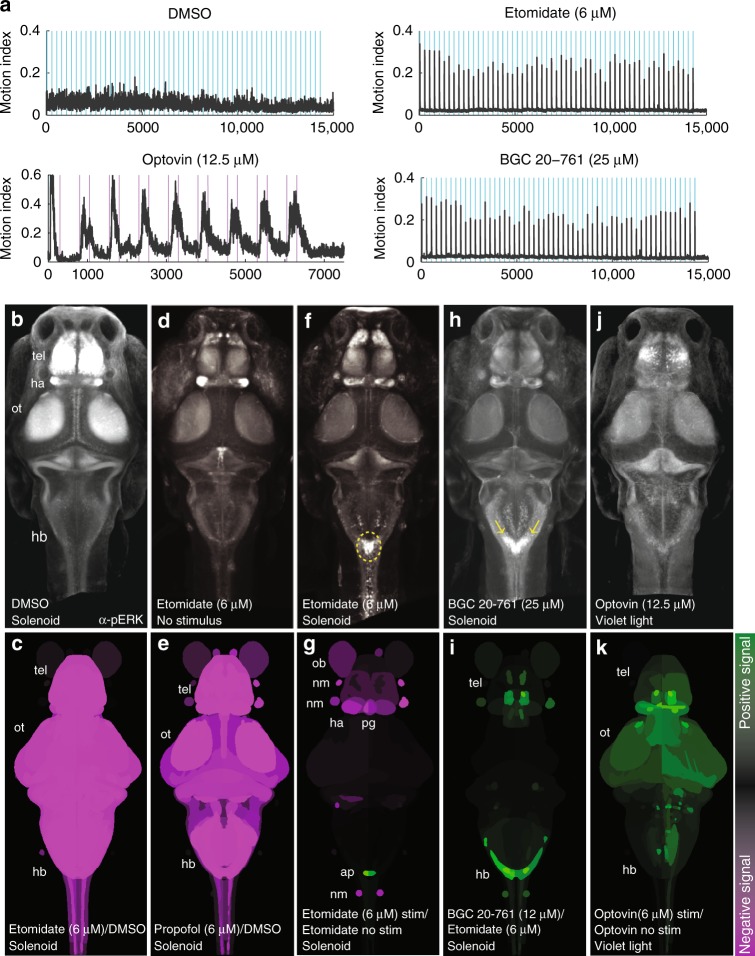
Fig. 5.
Hit compounds activate hindbrain neurons. Animals were exposed to the indicated drugs and stimuli and analyzed for pERK levels as a readout of neuronal activity. a Plots showing motor activity (y-axis) over time (x-axis) for animals treated with the indicated compounds (n = 25–50 larvae) in response to the indicated acoustic (blue) or violet light (purple) stimuli. b, d, f, h, j Confocal projections showing the average fluorescent intensity of image registered larval brains stained with α-pERK (n = 10 larvae/condition). Larvae were treated with the indicated compounds and exposed to the low-amplitude acoustic stimulus once every 10 s for 10 min, except for (b, no stimulus) and (f, violet light exposure). c, e, g, i, k Brain activity maps showing significant ΔpERK signals using the Z-brain online reference tool (n = 5–10 animals/condition). The heatmap indicates positive (green), negative (purple), and nonsignificant (black) changes in pERK labeling (P < 0.0005, Mann–Whitney U test). All activity maps are comparisons between the indicated treatment conditions. Abbreviations: tel, telencephalon; ot, optic tectum; hb, hindbrain; ob, olfactory bulb; nm, neuromast; ap, area postrema; pg, pineal gland