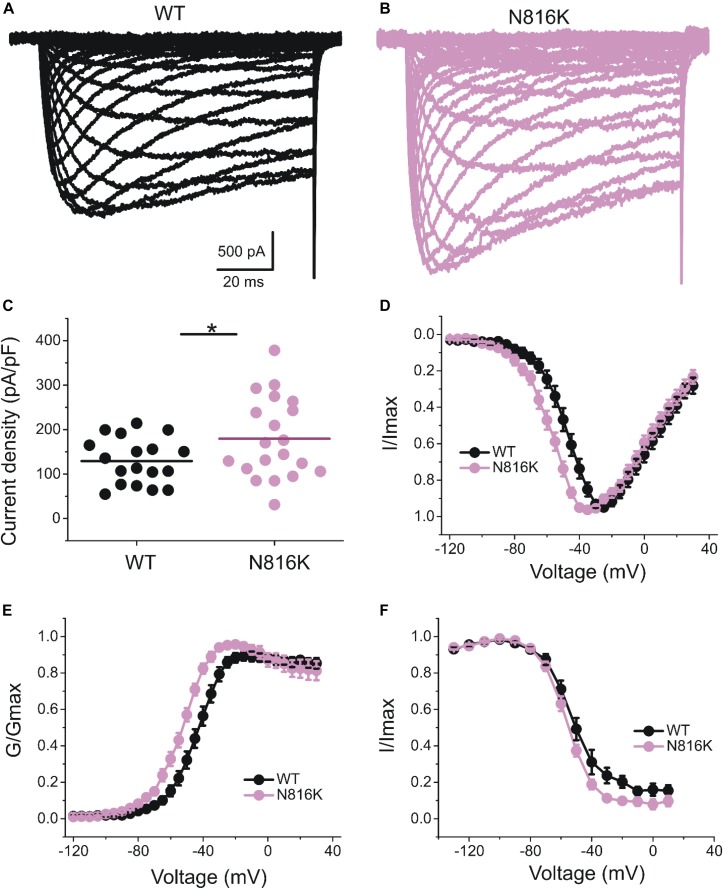
FIGURE 2.
N816K mutation hyperpolarizes voltage-dependence of activation of hNav1.9 channels in small DRG neurons. Representative traces showing characteristic human Nav1.9 currents from small DRG neurons expressing (A) wild-type (WT) or (B) N816K mutant Nav1.9 channels in adult Nav1.9-null mice. (C) Scatter plot of current densities, determined by normalization of peak current to cell capacitance, in small DRG neurons expressing WT and N816K mutant hNav1.9 channels. Solid lines indicate mean current densities. ∗p < 0.05. (D) Current-voltage relationships (I–V curves) for WT and N816K mutant hNav1.9 channels. Normalized peak inward current was plotted against voltage commands. N816K mutation hyperpolarizes the I–V curve of Nav1.9 channels. Boltzmann fits for activation (E) and steady-state fast-inactivation (F) show that N816K hyperpolarizes voltage-dependence of activation of Nav1.9 channels, but does not significantly change voltage-dependence of steady-state fast inactivation.