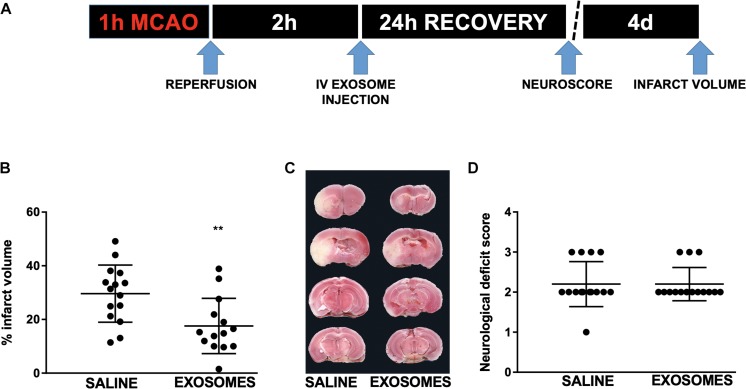
FIGURE 4.
Effect of post-injury intravenous treatment with exosomes from mouse NSCs on in vivo injury from transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). (A) Injury and treatment workflow. Mice were subjected to 1 h MCAO and treated after 2 h reperfusion with either intravenous (IV) saline or exosomes derived from mouse NSCs. (B) Quantification of infarct volume 4 days after MCAO in mice treated with either saline or mouse NSC-derived exosomes. (C) Representative TTC-stained brain sections with saline or exosome treatment (infarcted areas are lighter in color). (D) Neurological deficit 24 h following MCAO in mice treated with saline or NSC-derived exosomes. Data are expressed as mean ± SD, ∗∗p < 0.0046 versus saline (control) and exosome; n = 15–14/treatment group. TTC = 2,3,5-Triphenyltetrazolium chloride.