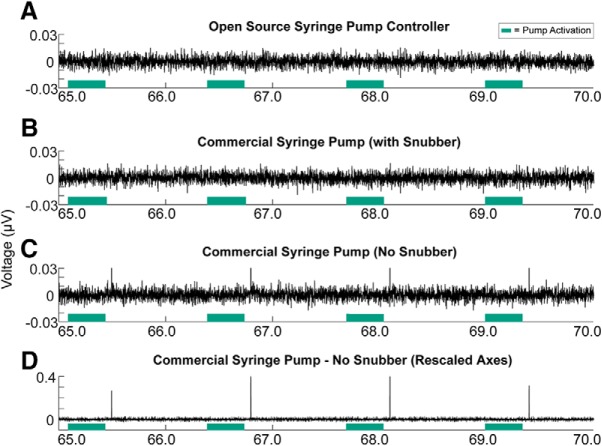
Figure 5.
Comparison of open source syringe pump controller against a commercial syringe pump in electrophysiological recordings. A, Electrophysiological recordings were made for 2 min, while the open source syringe pump controller was activated 100 times for 300 ms. The open source syringe pump controller did not produce any electrical transients, similar to in Figure 4C. B, When testing a standard commercial syringe pump in the same manner, electrical transients (called shot noise) were apparent within 100 ms after the syringe pump turned off. C, A zoomed-out view with rescaled axes shows the electrical transients across 5 s of recordings. D, An RC snubber/arc suppressor was added into the commercial syringe pump, which effectively suppressed transients. Green boxes designate when the syringe pump was activated with the motor running.