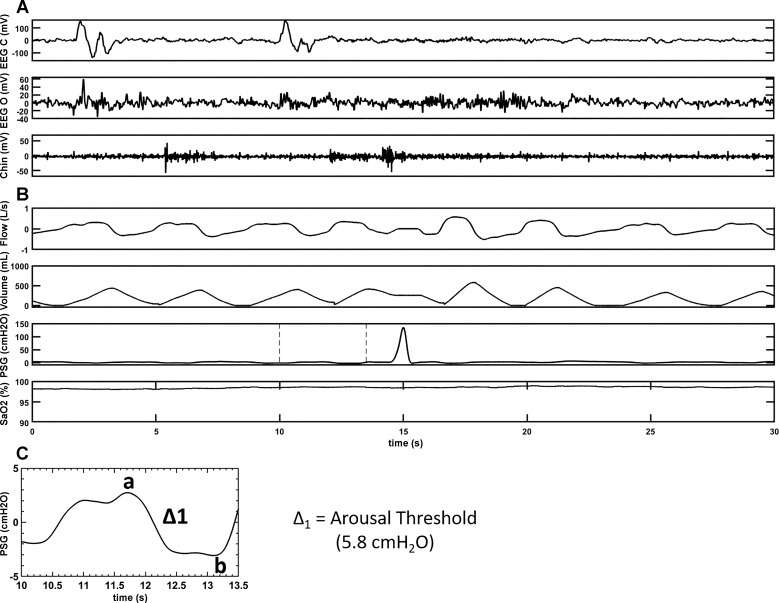
Fig. 2.
A representative polygraph record of a swallow with an AS during sleep in an able-bodied subject. A: brain electrical activity during sleep in two separate EEG channels, EEG(c) [records brain activity from electrode attached to the scalp near central (top) portion of the brain] and EEG(o) [records brain activity from electrode attached to the scalp near occipital (back) portion of the brain], respectively. A also shows muscle tension in the body during sleep via activity in the chin channel. B: respiratory parameters (flow, volume, and SaO2) during sleep along with the supraglottic pressure channel, which is the main channel to depict swallow (a positive spike on the supraglottic pressure channel) during sleep. C: magnification of the highlighted portion of the PSG channel of B to calculate the delta pressure change (Δ1 = a–b) for the breath before arousal preceding a swallow. A and B are representatives of a sleep segment recorded on two separate sleep systems, which are time matched. AS, arousal preceding the swallow; EEG(c), electroencephalogram (central); EEG(o), electroencephalogram (occipital); SaO2, oxygen saturation.