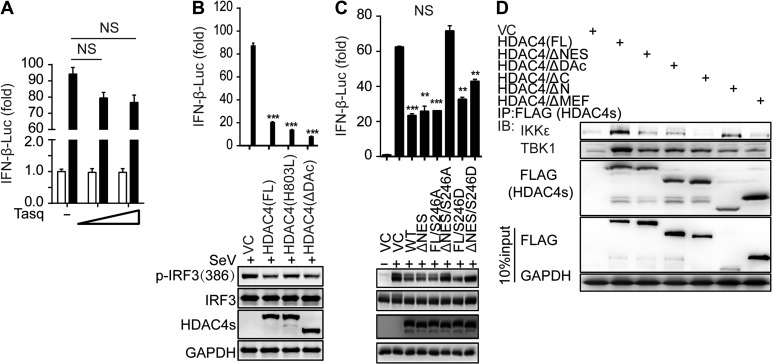
Figure 5.
Mapping the binding domain of HDAC4 interaction with TBK1/IKKε. (A) Luciferase assay analysis of IFNB1 promoter activity in HEK293T cells transfected for 24 h with a luciferase reporter plasmid, plus the HDAC4-specific inhibitor Tasquinimod (Tasq) (wedge:50 and 200 μM), and then left uninfected or infected for 8 h with SeV. (B and C) Luciferase assay analysis of IFNB1 promoter activity and IB analysis of phosphorylation of IRF3 at Ser386, IRF3, mutant HDAC4 containing various domain combinations (as in Supplementary Figure S4A) and GAPDH in HEK293T cells transfected for 24 h with luciferase reporter plasmid of IFN-β (IFN-β-Luc), together with various mutant HDAC4, and then infected for 8 h with SeV. (D) IB analysis of HEK293T cells transiently transfected for 48 h with vector encoding Flag-tagged full-length or mutant HDAC4 (as in Supplementary Figure S4A) and HA-tagged IKKε or TBK1, followed by IP analysis with Flag antibody and IB analysis with HA antibodies to IKKε and TBK1. NS, not significant (P > 0.05), *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 (unpaired t-test). Data are representative of three independent experiments with similar results (B−D) or from three independent experiments (A and histograms in B and C; mean ± SD).