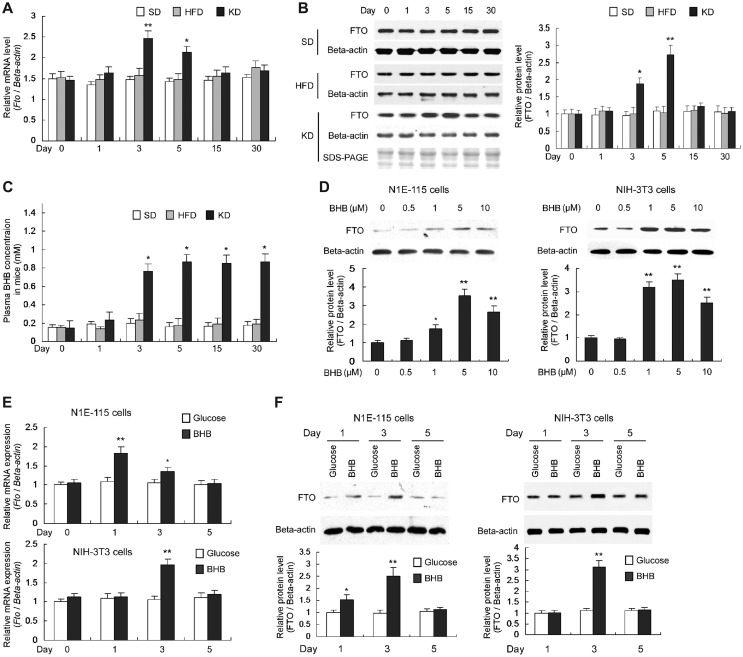
Figure 1.
KD-derived BHB transiently increases Fto expression. (A) Fto mRNA levels in the hypothalamus, normalized to β-actin mRNA level. n = 5, *P < 0.01, **P < 0.001, compared with the mRNA levels in SD-fed mice at the same time point. (B) FTO protein levels in the hypothalamus, normalized to β-actin protein. n = 3, *P < 0.01, **P < 0.001, compared with the protein levels in mice at Day 0 (as ‘1’). (C) BHB levels in the serum of peripheral blood. n = 5, *P < 0.001, compared with that in SD-fed mice at the same time point. (D) Mouse N1E-115 and NIH-3T3 cells were cultured in the medium with BHB instead of glucose and the protein levels were determined using western blot after 48 h. FTO protein levels (normalized to the β-actin protein) gradually increased in response to the rise of BHB concentrations. n = 3, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, compared with the protein levels in cells at Day 0 (as ‘1’). (E and F) N1E-115 and NIH-3T3 cells were cultured in the medium with BHB or glucose. BHB transiently increased Fto mRNA (E) and FTO protein (F) levels in N1E-115 cells after 1- and 3-day culture while in NIH-3T3 cells only after 3-day culture. The Fto mRNA and FTO protein levels were normalized to that of β-actin gene and β-actin protein, respectively. n = 3, *P < 0.01, **P < 0.001, compared with the mRNA or protein level in cells with glucose medium at the same time point.