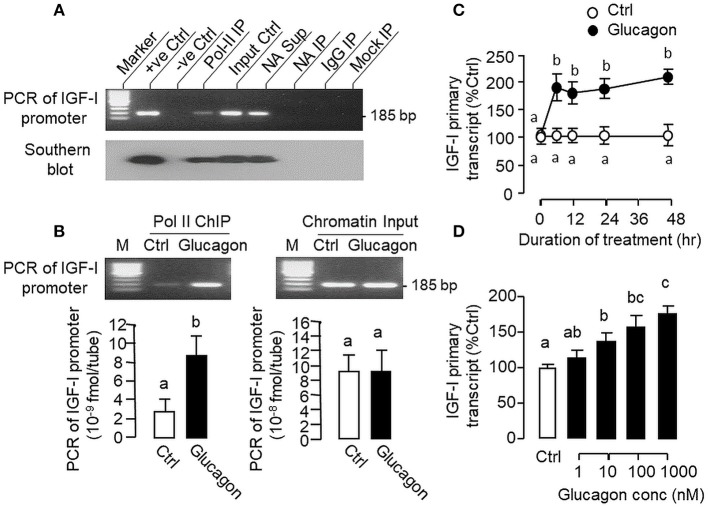
Figure 10.
Glucagon-induced Pol-II recruitment to IGF-I promoter and production of IGF-I primary transcript in carp hepatocytes. (A) Pol-II binding with IGF-I promoter revealed by PCR coupled with chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP). Chromatin samples with fragment size of 0.5–0.8 kb after sonication were prepared from carp hepatocytes and used for ChIP with the antibody for RNA Po-II (as “Pol-II IP”). After decrosslinking, PCR was performed using primers covering the proximal region of the carp IGF-I promoter. In this experiment, genomic DNA (as “+ve Ctrl”), chromatin input (as “Input Ctrl”) and “supernatant” of chromatin sample after IP with no antibody (as “NA Sup”) were used as the positive control. PCR without adding the template (as “–ve Ctrl”) or with chromatin samples after IP with “No Antibody” (as “NA IP”)/parallel ChIP with antibody for mouse IgG (as “IgG IP”) or without chromatin input (as “Mock IP”) were used as the negative control. The authenticity of PCR products detected was also confirmed with Southern blot using a DIG-labeled probe covering the same region of the IGF-I promoter. (B) Glucagon-induced Pol-II recruitment to IGF-I promoter in carp hepatocytes. Hepatocytes were challenged for 1 h with glucagon (10 nM) and subjected to chromatin preparation followed by ChIP with Pol-II antibody. After that, real-time PCR with primers covering the proximal region of IGF-I promoter was performed for quantitation of IGF-I promoter pulled down with RNA Pol-II. Real-time PCR for IGF-I promoter was also conducted in the chromatin input prior to Pol-II ChIP to serve as the loading control. (C) Time course and (D) Dose dependence of glucagon treatment on IGF-I primary transcript expression in carp hepatocytes. For the time course experiment, the dose of glucagon used was fixed at 100 nM for the duration as indicated, while the duration of drug treatment was fixed at 12 h for the dose-response study. After that, total RNA was isolated, digested with DNase I to remove genomic DNA contamination, and subjected to real-time PCR using primers covering the junction of exon III and intron III of carp IGF-I gene.