Figure 3.
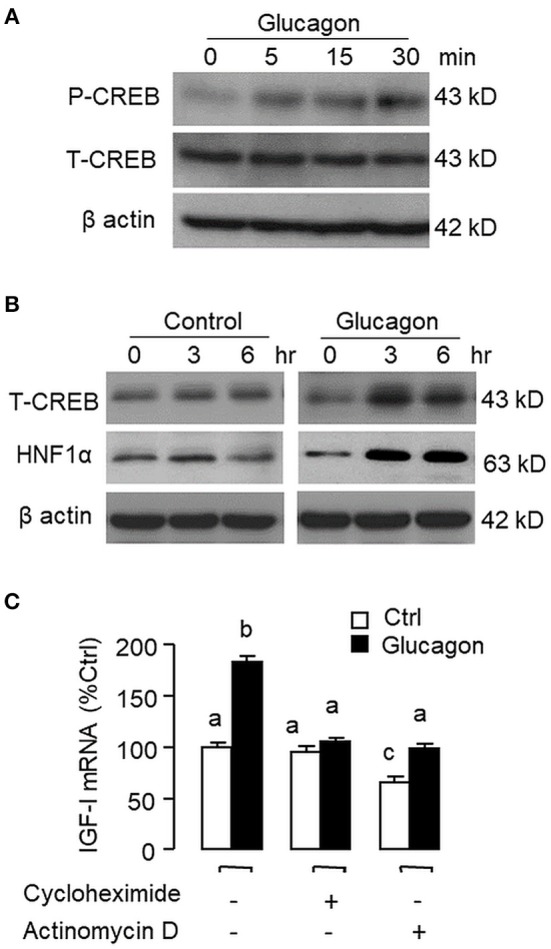
Glucagon-induced HNF1α and CREB expression in carp hepatocytes and function role of gene transcription and protein synthesis in the corresponding responses for IGF-I transcript. (A) Short-term treatment of glucagon (10 nM, up to 30 min) on CREB phosphorylation. (B) Long-term treatment of glucagon (10 nM, up to 6 h) on HNF1α and CREB protein expression. In these experiments, cell lysate was prepared from carp hepatocytes after drug treatment at the time points as indicated and subjected to Western blot using antibodies for phosphorylated CREB (as “P-CREB”) and total protein for CREB (as “T-CREB”) and HNF1α, respectively. Parallel blotting for β actin was also conducted to serve as the internal control. (C) Blocking gene transcription and protein synthesis on glucagon-induced IGF-I mRNA expression. Hepatocytes were challenged with glucagon (10 nM) for 12 h in the presence of the transcriptional inhibitor actinomycin D (8 μM) or protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide (10 μg/ml). After drug treatment, total RNA was isolated from individual wells and used for real-time PCR with primers specific for IGF-I transcript.
