Figure 5. Lactic acid suppresses NFκB function and miR-155 expression.
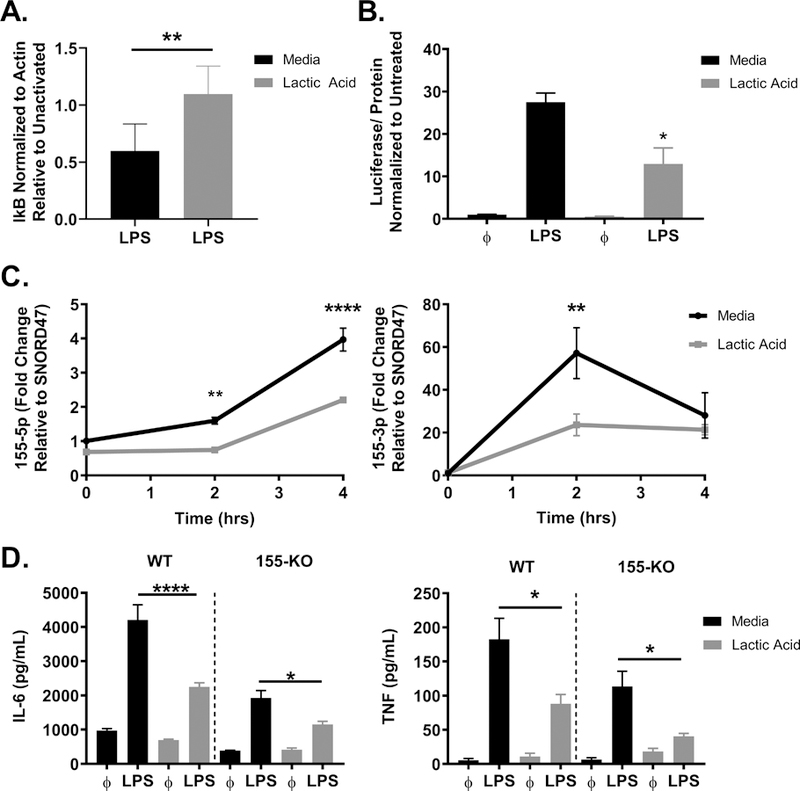
A) BMMC were treated ± lactic acid (12.5 mM) for 24 hours, then activated ± LPS (1 μg/mL) for 30 minutes. IκB degradation was determined by LPS-activated expression normalized to β-actin and relative to unstimulated controls. B) NFκB-luc transgenic BMMC were treated ± lactic acid (12.5 mM) for 24 hours, then activated ± LPS (1 μg/mL) for 2 hours. Luciferase activity was measured with the Promega Luciferase Assay Substrate and Glomax Luminometer. C) BMMC were cultured ± lactic acid (12.5 mM) for 24 hours, then activated ± LPS (1 μg/mL) for 2–4 hours. miRs were measured via qPCR and normalized relative to SNORD47. D) C57Bl/6 or miR-155 KO BMMC were treated ± lactic acid (12.5 mM) for 24 hours and activated ± LPS (1 μg/mL) for 16 hours. ELISA was used to measure cytokine concentrations in the cell supernatant. Data are means ± SEM of 3 populations, representative of 2 (A) 3 (B-D) independent experiments. *p < .05, **p < .01, ****p < .0001
