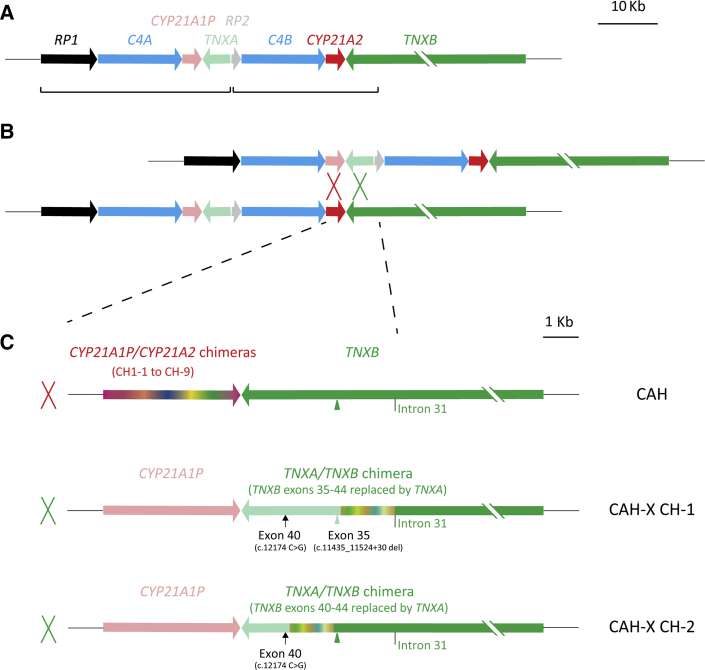
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) and CAH-X chimeric genes. A: Typical bimodular RCCX module: each pair of the homologous genes is shown in similar colors, with lighter colors representing pseudogenes; two RCCX units vulnerable for gene conversion are in brackets. B: Unequal crossover between CYP21A1P and CYP21A2 or TNXA and TNXB results in a commonly termed 30-Kb deletion CAH genotype. Dashed lines denote the window for unequal crossovers leading to CAH genotypes of 30-kb deletion. C: Schemes of three major subtypes of 30-Kb deletion: CYP21A1P/CYP21A2 chimeric genes with intact TNXB, pathogenic for CAH (top row); CYP21A1P-TNXA/TNXB chimera CAH-X CH-1 with TNXB exons 35–44 replaced by TNXA causes CAH-X due to tenascin-X haploinsufficiency (middle row); CYP21A1P-TNXA/TNXB chimera CAH-X CH-2 with TNXB exons 40-44 replaced by TNXA causes CAH-X due to a dominant negative effect (bottom row). CAH-X CH-1 has an exon 35 c.11435_11524+30 deletion (light green arrowhead) and an exon 40 c.12174 C>G mutation (arrow) in tandem, whereas CAH-X CH-2 has an intact exon 35 (green arrowhead) and an exon 40 c.12174 C>G mutation. The junction site window for each chimeric gene is shown in chameleonic colors. Schemes from CYP21A1P to TNXB intron 31, which is the boundary of RCCX module homologous repeats, are shown in scale. The size of TNXB is 68 Kb. CAH-X, a connective tissue dysplasia consistent with hypermobility-type Ehlers-Danlos syndrome due to a contiguous gene deletion involving the adjacent CYP21A2 and TNXB genes; CAH-X CH-1, CYP21A1P-TNXA/TNXB chimera with TNXB exons 35-44 replaced by TNXA; CAH-X CH-2, CYP21A1P-TNXA/TNXB chimera with TNXB exons 40-44 replaced by TNXA.