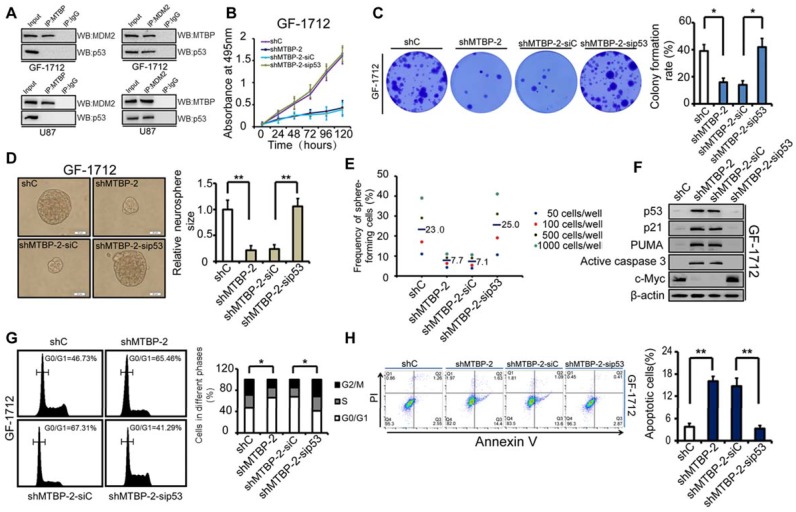
Figure 6.
Influence of p53 expression on the pro-survival effect of MTBP in GF-1712 cells. A: MTBP bound to MDM2 but not to p53, whereas MDM2 bound to both MTBP and p53 in GF-1712 and U87 cells as shown by co-immunoprecipitation. B: Effect of p53 silencing on the cell viability of MTBP-knockdown GF-1712 cells. C: Effect of p53 silencing on the colony formation of MTBP-knockdown GF-1712 cells as assessed by soft agar colony assays. D: Representative images of GF-1712 neurospheres transduced with indicated plasmids (left) and quantification of relative neurosphere sizes of indicated GSCs (right). Scale bar: 20 μm. E: Effect of p53 silencing on clonogenicity in MTBP-knockdown GF-1712 cells as determined by limiting dilution neurosphere forming assays. F: Effect of p53 silencing on the expressions of p21, PUMA, active caspase3, and c-myc in MTBP-knockdown GF-1712 cells as established by western blotting analyses. G: Effect of p53 silencing on G0/G1 arrest in MTBP-knockdown GF-1712 cells as shown by flow cytometry. H: Effect of p53 silencing on apoptosis in MTBP-knockdown GF-1712 cells. Results are presented as mean ± SEM of triplicate samples from three independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P < 0.01.