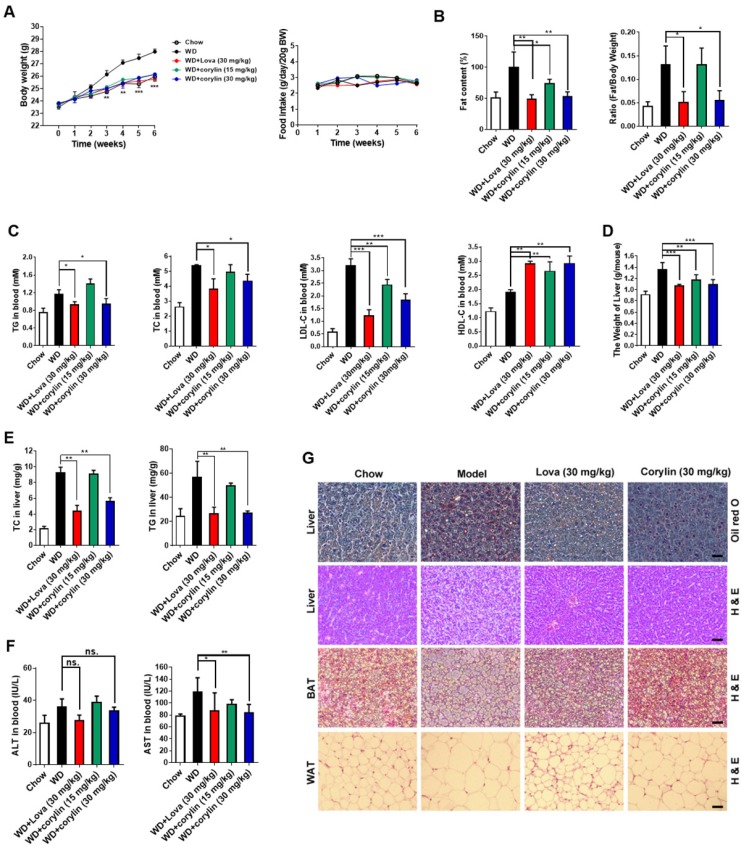
Figure 6.
Corylin Improves Lipid Homeostasis in WD-fed mice. Male C57BL/6J mice at 6 weeks of age were randomly grouped (n=6). Mice were allowed ad libitum access to water and different types of diets (WD, western-type diet). Vehicle (0.5% CMC-Na), corylin (15 or 30 mg/kg), or lovastatin (30 mg/kg) was administrated to mice by gastric irrigation every day. After 6 weeks treatment, the mice were sacrificed and subjected to a series of analysis as indicated below. (A) Food intake and body weight. (B) The ratio of fat and body weight or lean. (C) Effect of corylin on serum TG, TC, LDL-c and HDL-c levels. (D) The weight of liver. (E) Effect of corylin on TG and TC levels in the liver. (F) Effect of corylin on Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) in the serum. (G) Oil red staining in liver and histological analysis of liver, WAT and BAT. Error bars are represented as mean ± SEM. Statistical analyses were done with two-way ANOVA (Bonferroni's test) (A) or one-way ANOVA (Dunnett's post test) (B-G). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs WD.