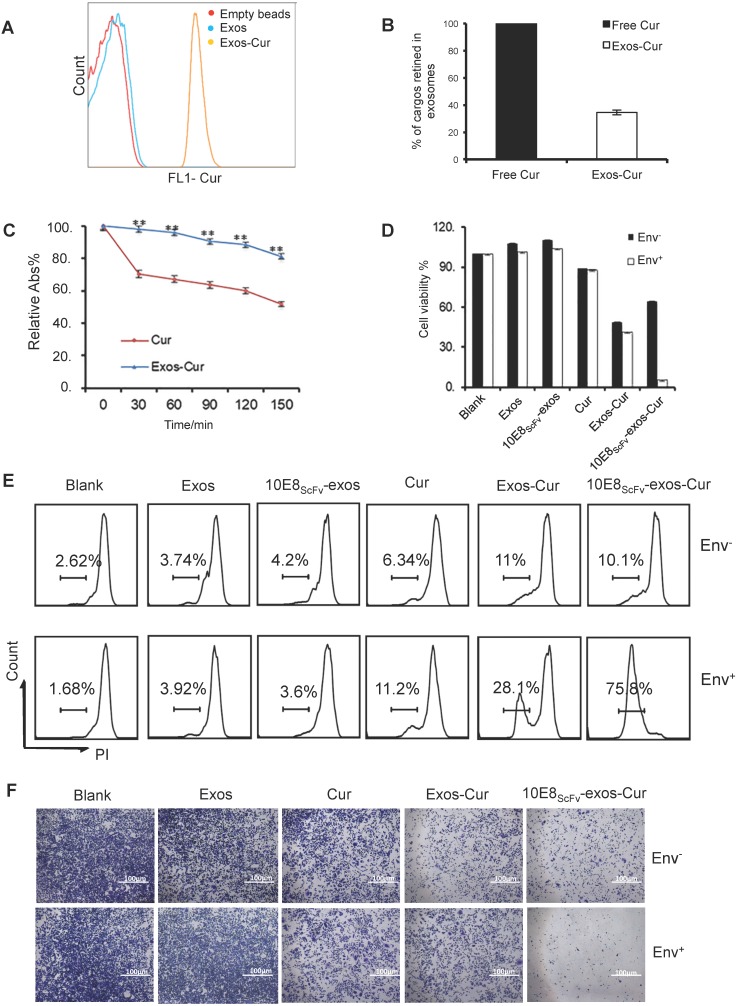
Figure 4.
Characterization of 10E8scFv-exos-Cur. (A) Flow cytometric analysis of exosomal curcumin (Cur). Vesicles were embedded into 4 μm beads. Cur staining was used for detection of exosomes and compared with control exosomes and empty beads. (B) The encapsulated efficiency (EE) of Cur cargoes in the exosomes was determined by absorbance spectrophotometry. EE (%) = ODExos-Cur / ODCur. OD of free Cur in loading process was set as control. (C) Stability of Exos-Cur were tested in comparison with free Cur. Cur and 10E8scFv-exos-Cur were suspended in PBS and incubated in the dark at 37℃. Absorbance curves at 421 nm show their concentration changes for the duration of 150 min. Data are mean ± SEM. Relative Abs (%) = (OD test - OD background ) / (OD start - OD background). (D) In vitro cellular cytotoxicity of Cur delivered by 10E8scFv-exos was tested by the measurement of cell viability. Env+ or Env- cells were incubated with medium (control), Exos, Exos-Cur, 10E8scFv-exos, 10E8scFv-exos-Cur, or free Cur for 24 h. Cur content in various preparations was adjusted to 15 μM. Cell viability was assessed using an MTT assay. 10E8scFv-exos-Cur showed higher cell killing of Env+ cells, as compared with free Cur at the corresponding concentration, which showed almost no cell killing. (E) Env+ or Env- cell lines were treated with medium (control), Exos, Exos-Cur, 10E8scFv-exos, 10E8scFv-exos-Cur, or free Cur for 16 h. Cur content in various preparations was adjusted to 15 μM. Cell death was measured by PI staining and flow cytometry. Numbers shows the ratio of staining of PI in the treated cells. (F) Colony formation of the Env- or Env+ cells treated exosomes were investigated. The sham groups were used as negative control. Data are mean ± SEM.