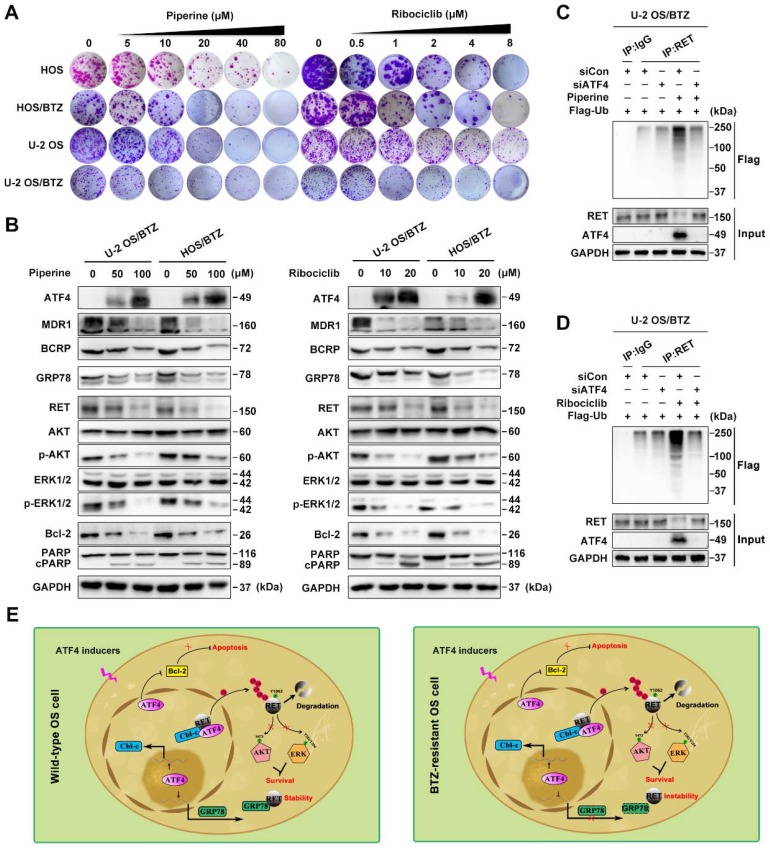
Figure 8.
ATF4 activator screening from a compound library. A, Proliferation of control or piperine and ribociclib-treated OS and OS/BTZ cells was evaluated by colony formation assays. B, BTZ-resistant OS sublines were cultured in medium containing the indicated concentrations of piperine and ribociclib for 2 days, and lysates were blotted for the indicated proteins. C and D, ATF4 was knocked down in U-2 OS/BTZ cells, and then the cells were treated with piperine or ribociclib. Lysates were harvested from cells for immunoprecipitation with anti-RET antibody. IP samples were used to study ubiquitinated RET levels by western blotting with anti-FLAG antibody. E, Model indicating that the regulation of RET signalling by ATF4 leads to drug sensitivity in osteosarcoma. In wild-type OS cells, ATF4 promotes Cbl-c transcription and recruits it to synergistically to bind to RET by inducing the nuclear translocation of RET, thus resulting in the degradation of RET and inactivation of downstream signalling. Meanwhile, ATF4-transactivated GRP78 competitively interacts with RET, which is beneficial for RET stabilization. In contrast, ATF4 specifically transcriptionally inhibits GRP78 in BTZ-resistant OS cells, represents reinforced function of overwhelming RET signaling for the prevention of cancer malignancy drug resistance.