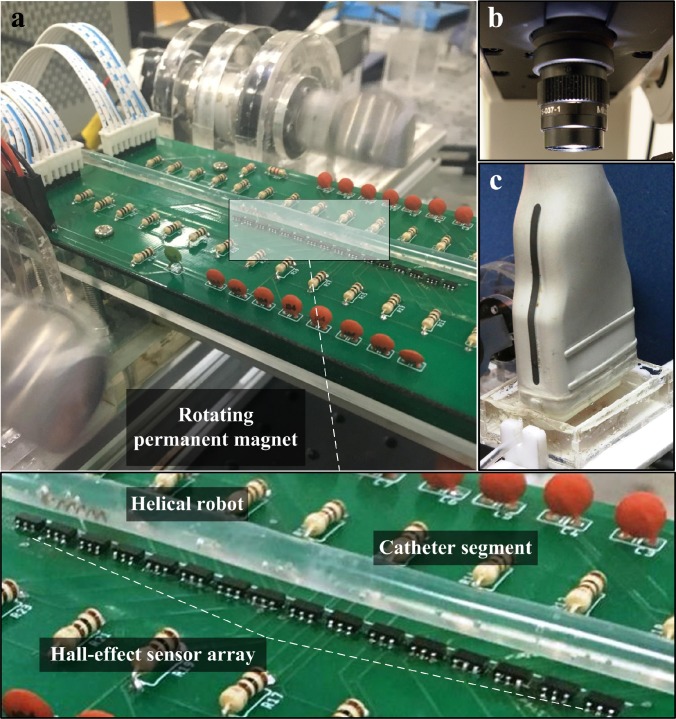
FIG. 2.
A permanent magnet-based robotic system enables a helical robot to swim using rotating magnetic fields. (a) A catheter segment is aligned with an array of Hall-effect sensors (3D magnetic sensor TLV493D-A1B6, Infineon Technologies AG, Munich, Germany). Position of the helical robot inside the catheter segment is estimated using measurements of these sensors and the precalculated magnetic field map of the rotating permanent magnets. (b) Position of the helical robot is measured with a high-speed camera (avA100-120kc, Basler Area Scan Camera, Basler AG, Ahrensburg, Germany) to validate the magnetic tracking. (c) An ultrasound transducer (LA523 linear array ultrasound transducer, Esaote, Italy) localizes the helical robot inside the ex vivo model.