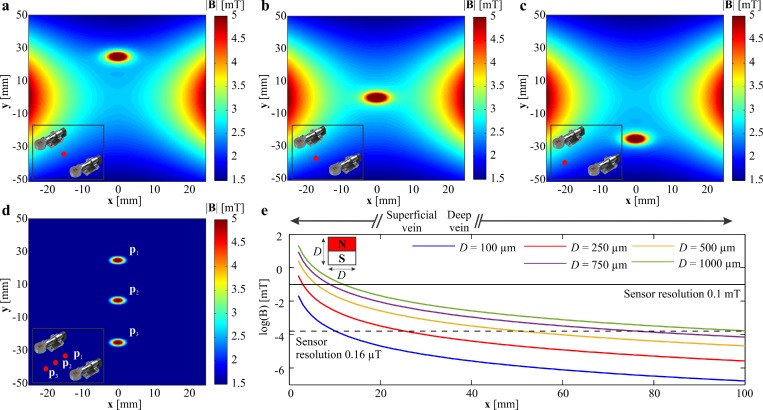
FIG. 4.
The precalculated magnetic field map of the two rotating permanent magnets (zero angular position) is superimposed to the helical robot's magnetic field and calculated at the plane of the Hall-effect sensor (x, y, 3) mm. The distance between the rotating permanent magnets is 15 cm. The positions of the permanent magnets are (±75, 0, 0) mm. (a) The helical robot is positioned at (0, 25, 0) mm. (b) The helical robot is positioned at (0, 0, 0) mm. (c) The helical robot is positioned at (0, −25, 0) mm. (d) The actuating magnetic field is subtracted from the total magnetic field to provide the robot's field at position (0, 25, 0) mm, (0, 0, 0) mm, and (0, −25, 0) mm, respectively. The red dot indicates the position of the helical robot between the rotating dipole fields. (e) Magnetic field is calculated vs the distance for permanent NdFeB cylindrical magnets with diameter and length D. The horizontal solid and dashed lines represent the theoretical resolution of 2 Hall-effect sensors with a resolution of 0.1 mT and 0.16 T, respectively.