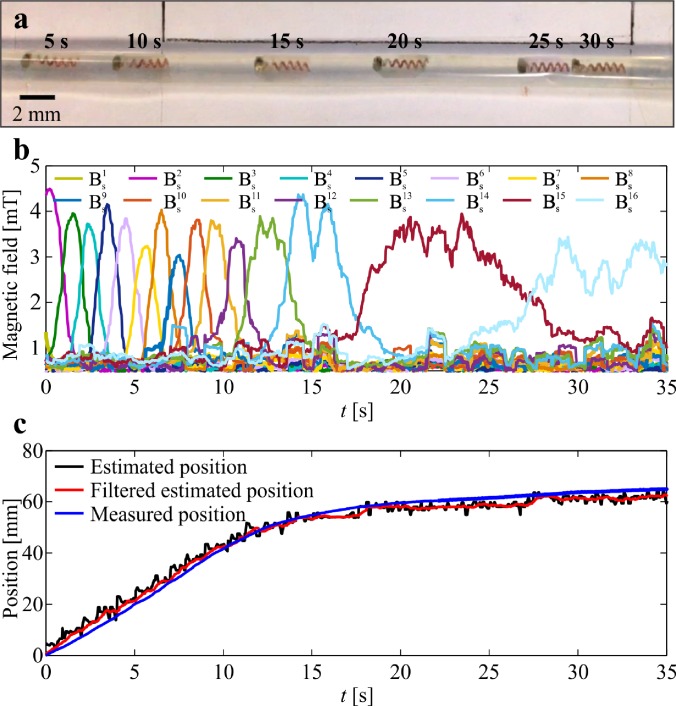
FIG. 5.
Position of a helical robot is tracked continuously during propulsion along a catheter segment. (a) The helical robot swims at an average speed of 4.2 mm/s under the influence of a rotating magnetic field at a frequency of 5 Hz. (b) Magnetic field is measured using an array of 16 Hall-effect sensors. is the magnitude of the three magnetic field components measured at the ith sensor. (c) The estimated position (filtered using 15-point moving average filter) of the helical robot is compared to the measured position using computer vision. The absolute position error is 2.32 mm. (See the supplementary material video).